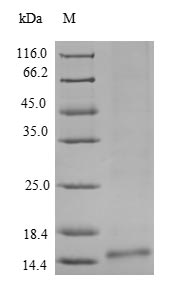
Recombinant Ceratopteris richardii Cyanovirin-N homolog gets expressed in a yeast system and includes the full mature protein from amino acids 28 to 142. The product comes with an N-terminal 6xHis-tag that makes purification and detection more straightforward. SDS-PAGE analysis shows it reaches a purity level greater than 90%, which appears suitable for various research applications. This protein is meant for research use only and isn't intended for therapeutic or diagnostic purposes.
Cyanovirin-N homolog is a protein that seems particularly good at binding specific sugar molecules—a property that may influence various biological processes. Scientists study proteins in the Cyanovirin-N family mainly for their roles in carbohydrate recognition and binding pathways. This makes them quite interesting for research areas that focus on molecular interactions and the development of new biotechnological applications.
Potential Applications
Note: The applications listed below are based on what we know about this protein's biological functions, published research, and experience from experts in the field. However, we haven't fully tested all of these applications ourselves yet. We'd recommend running some preliminary tests first to make sure they work for your specific research goals.
Based on the provided information, recombinant Ceratopteris richardii Cyanovirin-N homolog is produced in a yeast expression system as the full-length mature protein (28-142aa) with an N-terminal 6xHis-tag. Cyanovirin-N homologs are lectin proteins that require precise folding and disulfide bond formation for their carbohydrate-binding activity. Yeast expression systems provide eukaryotic folding machinery capable of supporting disulfide bond formation, which is critical for this protein's structural integrity. The full-length mature protein increases the probability of correct folding. However, the N-terminal His-tag may potentially interfere with protein function or folding. Purity >90% by SDS-PAGE is determined under denaturing conditions and does not confirm native folding or bioactivity. No validation data (e.g., carbohydrate binding assays, circular dichroism) are provided. Therefore, while yeast expression offers advantages for proper folding, the protein's structural and functional integrity cannot be confirmed without experimental validation.
1. Lectin-Carbohydrate Interaction Studies
Lectin function depends on a precise three-dimensional structure; misfolding would compromise carbohydrate recognition. If correctly folded, this recombinant protein can be used to study carbohydrate binding specificity and affinity through techniques like glycan array screening or surface plasmon resonance. However, if misfolded, the carbohydrate-binding domains may be disrupted, leading to invalid binding data and incorrect evolutionary comparisons with other cyanovirin-N proteins.
2. Protein-Protein Interaction Mapping
Protein-protein interactions require native conformation; structural defects would yield misleading interaction networks. If properly folded, the His-tagged protein can be used in pull-down assays to identify biological interaction partners. However, if misfolded, interaction domains may be altered, resulting in non-specific binding or failure to identify genuine partners in fern biology.
3. Structural and Biophysical Characterization
Structural studies require proper folding to generate biologically relevant data. If correctly folded, the protein is suitable for structural studies like X-ray crystallography or NMR, and biophysical analysis like circular dichroism. However, if misfolded, structural data would misrepresent the native protein's architecture, leading to erroneous structure-function insights.
4. Antibody Development and Immunoassay Applications
Antibodies can be generated against linear sequences even in misfolded proteins, but may lack specificity for native conformation. This application is suitable, as antibody generation primarily relies on linear epitope recognition. However, if misfolded, antibodies may not optimally recognize conformational epitopes of the native protein in biological contexts.
Final Recommendation & Action Plan
Before employing this recombinant protein in functional studies, validate its folding and bioactivity through biophysical methods (circular dichroism for secondary structure, disulfide bond analysis) and functional assays (carbohydrate binding tests); if validation confirms proper folding, proceed with applications while considering potential tag interference; if misfolded, consider tag removal or alternative expression systems; antibody development can proceed immediately but validate antibodies against native protein; always include appropriate controls (e.g., known lectins, binding standards) in experiments to ensure reliability. For structural studies, consider removing the His-tag to avoid interference with protein crystallization or NMR analysis.