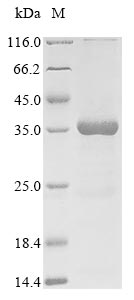
Recombinant Vaccinia virus IMV heparin-binding surface protein (H3L) is expressed in E. coli and includes the amino acid region 21-270. This partial-length protein is engineered with an N-terminal 10xHis-tag and a C-terminal Myc-tag for easier purification and detection. The protein achieves a purity greater than 85%, as confirmed by SDS-PAGE analysis, which appears sufficient for most research applications.
The Vaccinia virus IMV heparin-binding surface protein (H3L) plays a critical role in how the virus interacts with host cells, particularly through its binding affinity to heparin. This interaction seems vital for understanding viral entry and pathogenesis. H3L has become an important focus in virology research, likely providing insights into viral mechanisms and potential therapeutic targets.
Potential Applications
Note: The applications listed below are based on what we know about this protein's biological functions, published research, and experience from experts in the field. However, we haven't fully tested all of these applications ourselves yet. We'd recommend running some preliminary tests first to make sure they work for your specific research goals.
Vaccinia virus H3L is a viral envelope protein that requires precise folding, disulfide bond formation, and proper tertiary structure for its heparin-binding activity and viral entry functions. The E. coli expression system cannot provide the eukaryotic post-translational modifications and complex folding environment necessary for this viral surface protein. The dual N-terminal 10xHis-tag and C-terminal Myc-tag may sterically interfere with the protein's functional domains and binding sites. While the protein may be soluble, it is highly unlikely to achieve the correct folding needed for functional heparin-binding activity. The probability of correct folding with biological activity is low.
1. Antibody Development and Immunoassay Research
Antibody development relies on antigenic sequence recognition rather than functional folding. This recombinant H3L serves as an excellent immunogen for generating antibodies against linear epitopes of the vaccinia virus surface protein. The dual tags facilitate purification and provide additional epitopes for screening. However, antibodies may not efficiently recognize conformational epitopes on the native, properly folded viral protein.
2. Biochemical Characterization and Binding Assays
Basic biophysical characterization is possible, but functional binding studies are not feasible. Functional binding activity requires native protein conformation that E. coli cannot provide. Techniques like circular dichroism can analyze secondary structure, but heparin-binding assays will likely yield negative results due to probable misfolding.
3. Tag-Assisted Purification Method Development
Purification development depends on tag functionality rather than protein folding. This protein is ideal for developing and optimizing dual-tag purification protocols. The tags provide flexibility for testing different purification strategies and comparing tag efficiency.
Final Recommendation & Action Plan
The E. coli expression system is fundamentally unsuitable for producing a functional viral surface protein like H3L, limiting applications to non-functional uses. The immediate priority is basic biophysical characterization to assess the protein's physical properties. Applications 1 and 3 (antibody development and purification optimization) can proceed immediately. Avoid interaction studies and functional research due to the high probability of misfolding. For functional H3L studies, use mammalian or insect cell expression systems that can provide proper post-translational modifications and folding environment.