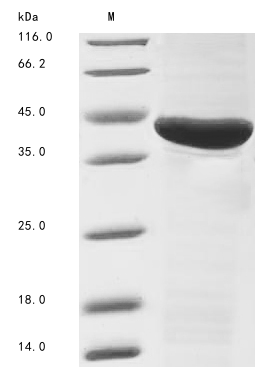
Recombinant Vespa magnifica Hyaluronidase is produced in E. coli and includes an N-terminal 6xHis-tag to simplify purification and detection. The product represents the full length of the mature protein, spanning amino acids 27 to 357. Purity levels exceed 85% as confirmed by SDS-PAGE, which appears to make it sufficiently reliable for research purposes. This product is designed exclusively for research use and is not intended for diagnostic or therapeutic applications.
Hyaluronidase from Vespa magnifica plays a key role in breaking down hyaluronic acid, a major component of the extracellular matrix. When this enzyme degrades hyaluronic acid, it may help other molecules or cells spread more easily through tissue. This characteristic suggests that hyaluronidase could serve as an important tool for studying tissue permeability and matrix biology, particularly in applications requiring enhanced tissue penetration.
Potential Applications
Note: The applications listed below are based on what we know about this protein's biological functions, published research, and experience from experts in the field. However, we haven't fully tested all of these applications ourselves yet. We'd recommend running some preliminary tests first to make sure they work for your specific research goals.
1. Biochemical Characterization
This recombinant hyaluronidase can be used for basic biophysical characterization, such as determining molecular weight, oligomeric state, and thermal stability using techniques like size-exclusion chromatography and circular dichroism. However, enzymatic activity studies (e.g., kinetic parameters, substrate specificity) are not recommended without prior validation of correct folding and activity, as the E. coli expression system likely produces a misfolded, inactive protein.
2. Antibody Development and Immunological Studies
This protein serves as an excellent immunogen for generating antibodies against linear epitopes of Vespa magnifica hyaluronidase. The full-length sequence ensures broad epitope coverage, and the high purity minimizes antibodies against contaminants. These antibodies will be useful for Western blotting and immunoassays under denaturing conditions.
3. Comparative Venom Component Analysis
This protein can be used for sequence-based comparisons and immunological cross-reactivity studies across species. However, comparative functional analyses (e.g., enzymatic activity differences) are invalid due to the likely misfolded state and lack of activity. Structural comparisons via SDS-PAGE or Western blotting are feasible.
Final Recommendation & Action Plan
The E. coli expression system is unsuitable for producing a functional hyaluronidase, limiting applications to non-functional uses. The immediate priority is to conduct biophysical characterization (Application 1) to assess the protein's folding state and stability. Application 2 (Antibody Development) can proceed immediately. Protein-protein interactions and inhibitor binding depend on precise tertiary structure, which this E. coli-expressed protein likely lacks. Functional comparisons require native, active enzymes, but sequence and immunological analyses are reliable based on the protein's primary structure. For reliable functional data, use hyaluronidase from eukaryotic expression systems or native venom purification.