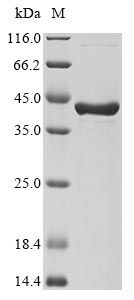
This recombinant chimeric Dpo4 protein comes from E. coli expression and contains the complete 1-353 amino acid sequence. The N-terminal 6xHis-tag makes purification and detection more straightforward. SDS-PAGE analysis shows the protein achieves over 90% purity, which appears to provide reliable performance for research work. This product is intended strictly for research purposes.
Dpo4 represents a DNA polymerase that plays a key role in translesion DNA synthesis. This process allows DNA replication to proceed past damaged sites that would normally cause the machinery to stall. As a Y-family polymerase, it likely contributes to how cells maintain their genomic integrity. Research into Dpo4's function and molecular interactions may be crucial for understanding DNA repair mechanisms and mutagenesis.
Potential Applications
Note: The applications listed below are based on what we know about this protein's biological functions, published research, and experience from experts in the field. However, we haven't fully tested all of these applications ourselves yet. We'd recommend running some preliminary tests first to make sure they work for your specific research goals.
Dpo4 is a Y-family DNA polymerase from Sulfolobus solfataricus that requires precise folding for its DNA binding and polymerase activity. The E. coli expression system is suitable for this archaeal protein as both are prokaryotic systems with similar folding environments. The chimeric nature of this construct may introduce some folding complexities, but the N-terminal 6xHis tag is small and unlikely to significantly interfere with functional domains. Given that Dpo4 and related polymerases have been successfully expressed in E. coli in numerous studies, this recombinant protein has a moderate to high probability of correct folding with functional activity, though experimental validation remains essential.
1. Protein Purification and Biochemical Characterization Studies
Biochemical characterization is essential for determining protein quality and should be performed first, regardless of functional status. Biochemical characterization provides essential data on folding quality and functional competence. If correctly folded (verified), the protein is excellent for detailed biophysical analysis, including thermal stability, oligomerization state, and cofactor binding studies. If misfolded/unverified, characterization still yields valuable physical property data for quality control.
2. Antibody Development and Immunological Studies
Antibody development relies on antigenic sequence recognition. If correctly folded (verified), the protein excels for generating conformation-sensitive antibodies. If misfolded/unverified, it remains suitable for producing antibodies against linear epitopes of the chimeric construct.
3. Protein-Protein Interaction Studies
Protein-protein/DNA interactions depend on a precise tertiary structure that must be confirmed. Polymerase interactions with DNA and protein partners require precise tertiary structure. If correctly folded (verified), the protein is suitable for identifying physiological interaction partners. If misfolded/unverified, there is a high risk of non-specific binding or interaction failure.
4. Comparative Structural and Functional Analysis
Meaningful comparative studies require native protein conformation. If correctly folded (verified), the protein enables valid structural and functional comparisons with wild-type Dpo4. If misfolded/unverified, comparative analyses would yield misleading results about engineering effects.
Final Recommendation & Action Plan
The E. coli expression system is generally suitable for this archaeal polymerase, but the chimeric nature of the construct requires experimental validation of folding and functional activity before reliable use in specific applications. Begin with Application 1 (Biochemical Characterization) to assess folding quality through size-exclusion chromatography, circular dichroism spectroscopy, and to validate DNA polymerase activity using standard polymerase assays. Once correct folding and functional activity are verified, proceed confidently with Applications 3 and 4 for interaction studies and comparative analyses. Application 2 (antibody development) can proceed immediately regardless of folding status. If misfolding is detected, limit applications to linear epitope antibody production and basic biophysical characterization, avoiding all functional interaction and comparative studies.