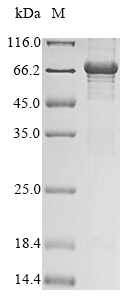
Recombinant Rat MICOS complex subunit Mic60 (Immt) is produced through an in vitro E.coli expression system and contains amino acids 34 to 609, which creates a partial protein product. The protein includes an N-terminal 10xHis-tag that helps with purification and detection. SDS-PAGE analysis shows the protein achieves a purity level exceeding 85%, making it what appears to be a solid choice for research applications targeting mitochondrial studies.
The MICOS complex subunit Mic60—also known as mitochondrial contact site and cristae organizing system—likely plays a crucial role in maintaining mitochondrial architecture. This protein seems particularly important in forming cristae junctions and organizing the mitochondrial inner membrane overall. Mic60's involvement in these processes may highlight why it's become significant in studies examining mitochondrial function and dynamics.
Potential Applications
Note: The applications listed below are based on what we know about this protein's biological functions, published research, and experience from experts in the field. However, we haven't fully tested all of these applications ourselves yet. We'd recommend running some preliminary tests first to make sure they work for your specific research goals.
Rat Mic60 (Immt) is a core component of the mitochondrial MICOS complex that requires precise folding, membrane integration, and specific protein-protein interactions for its function in mitochondrial cristae junction formation. The in vitro E. coli expression system (cell-free) cannot provide the necessary mitochondrial membrane environment, lipid interactions, or complex assembly conditions required for this integral membrane protein. The partial fragment (34-609aa) lacks the full structural context, and the N-terminal 10xHis-tag may interfere with the protein's membrane-targeting domains. While cell-free systems can produce soluble proteins, the probability of correct folding with functional membrane-organizing activity is extremely low.
1. Antibody Development and Validation
This application is highly suitable as antibody development relies on linear epitope recognition rather than functional protein folding. The partial fragment (34-609aa) provides specific epitopes within this region for antibody production, independent of native membrane integration or complex formation. The His-tag facilitates efficient purification and screening processes.
2. Structural and Biophysical Characterization
Basic biophysical characterization is limited to soluble fragment characterization only. It will not reflect native membrane protein structure. Techniques like circular dichroism can analyze secondary structure content, and size-exclusion chromatography can assess aggregation state, but results will describe a soluble fragment rather than the membrane-integrated protein. The absence of a lipid environment fundamentally alters the protein's structural properties.
Final Recommendation & Action Plan
The in vitro E. coli expression system is fundamentally unsuitable for producing a functional version of this mitochondrial membrane protein due to the absence of essential membrane environment and complex assembly factors. This recombinant Mic60 fragment is only suitable for Application 2 (antibody development against linear epitopes) and basic aspects of Application 3 (characterization of the soluble fragment's physical properties). Functional MICOS complex interactions require proper membrane integration and complex assembly that cannot be achieved in this expression system. A soluble, misfolded fragment of a membrane protein may expose hydrophobic regions leading to extensive non-specific binding, and the lack of mitochondrial context makes any interaction data biologically misleading for understanding MICOS complex formation. Mic60's membrane-organizing function requires proper integration into lipid bilayers and interaction with other MICOS components. A soluble, non-membrane-integrated fragment will not replicate the protein's native function in cristae junction formation, making functional assays biologically irrelevant.