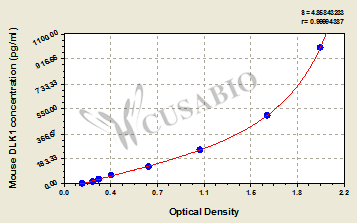
The mouse DLK1 ELISA Kit is used to quantitatively measure mouse DLK1 levels in serum, plasma, or tissue homogenates. It performs well in important characteristics, including sensitivity and specificity. This assay is based on the sandwich ELISA mechanism and enzyme-substrate chromogenic reaction. The solution color develops proportionally to the amount of DLK1 in the sample. And the intensity of the color can be measured at 450 nm via a microplate reader.
DLK1, a noncanonical ligand of notch signaling, plays an essential in normal developmental processes, including neuroendocrine differentiation, hepatocyte and biliary epithelial cell differentiation, hematopoiesis, osteogenesis, skeletal muscle differentiation, and chondrogenic differentiation. DLK1 is involved in the regulation of stem cell pools, tissue differentiation during development, cancer differentiation, and cancer stem-like cell (CSCs) maintenance. It has been detected in various carcinomas including neuroendocrine tumors.