Call us
301-363-4651 (Available 9 a.m. to 5 p.m. CST from Monday to Friday)
| Code | CSB-EL025383RA |
| Size | 96T,5×96T,10×96T |
| Price | Request a Quote |
| Trial Size |
24T ELISA Kit Trial Size (Only USD$150/ kit) * Sample kit cost can be deducted as a $30 credit for each 96-assay kit of the same analyte and brand you subsequently purchase within six months until depleted. More details >> Interested in a trial size? Please leave a message below.
|
| Have Questions? | Leave a Message or Start an on-line Chat |
| Intra-assay Precision (Precision within an assay): CV%<8% | |||||||
| Three samples of known concentration were tested twenty times on one plate to assess. | |||||||
| Inter-assay Precision (Precision between assays): CV%<10% | |||||||
| Three samples of known concentration were tested in twenty assays to assess. | |||||||
| To assess the linearity of the assay, samples were spiked with high concentrations of rat TXNIP in various matrices and diluted with the Sample Diluent to produce samples with values within the dynamic range of the assay. | |||||||
| Sample | Serum(n=4) | ||||||
| 1:1 | Average % | 91 | |||||
| Range % | 86-95 | ||||||
| 1:2 | Average % | 102 | |||||
| Range % | 97-107 | ||||||
| 1:4 | Average % | 91 | |||||
| Range % | 85-97 | ||||||
| 1:8 | Average % | 97 | |||||
| Range % | 91-103 | ||||||
| The recovery of rat TXNIP spiked to levels throughout the range of the assay in various matrices was evaluated. Samples were diluted prior to assay as directed in the Sample Preparation section. | |||||||
| Sample Type | Average % Recovery | Range | |||||
| Serum (n=5) | 90 | 85-96 | |||||
| EDTA plasma (n=4) | 92 | 87-97 | |||||
| These standard curves are provided for demonstration only. A standard curve should be generated for each set of samples assayed. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
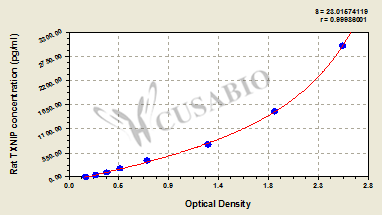
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
This Rat TXNIP ELISA Kit was designed for the quantitative measurement of Rat TXNIP protein in serum, plasma, tissue homogenates, cell lysates. It is a Sandwich ELISA kit, its detection range is 47 pg/mL-3000 pg/mL and the sensitivity is 11.75 pg/mL.
There are currently no reviews for this product.