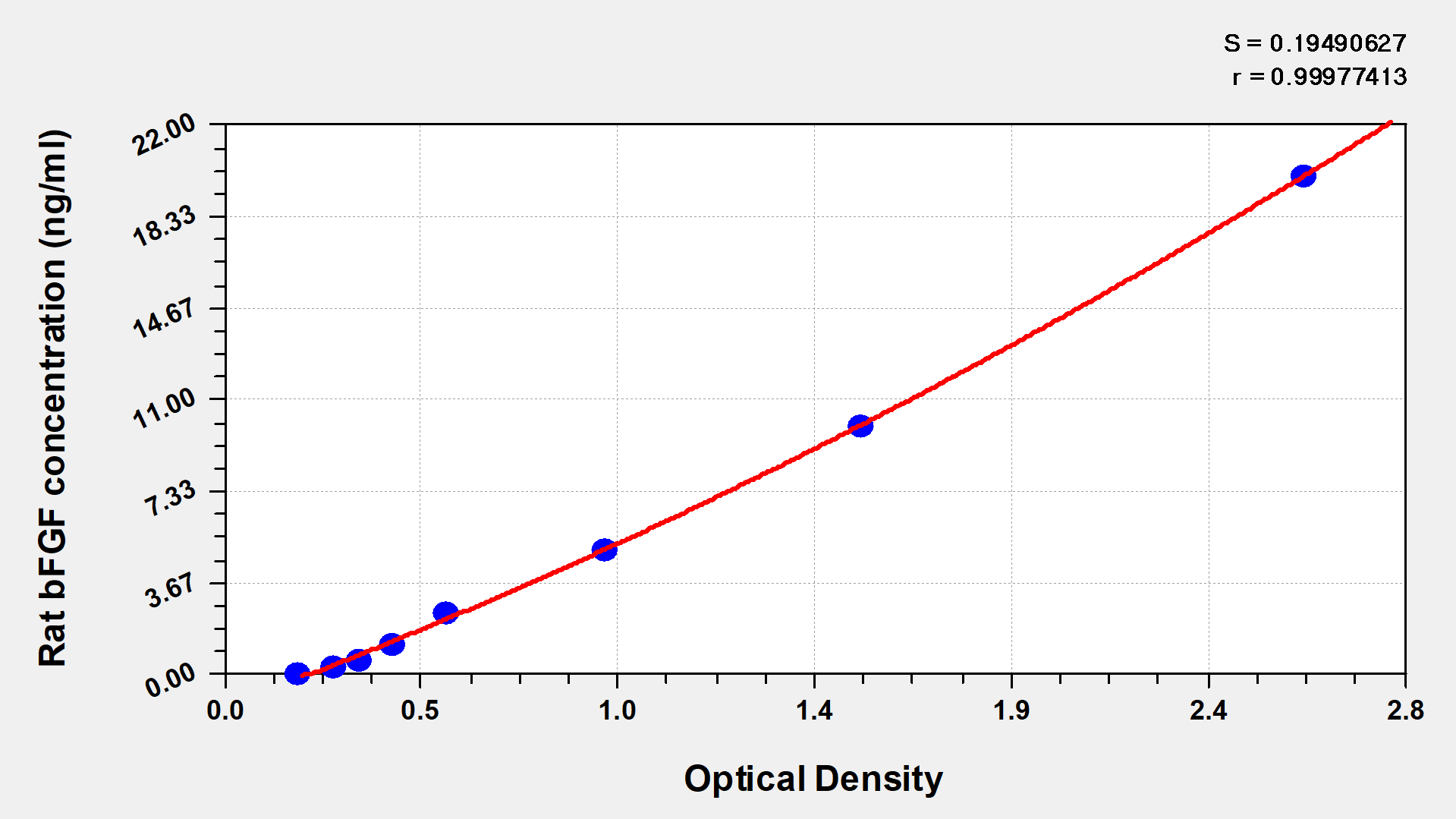
The rat bFGF ELISA Kit is engineered for accurate measurement of rat bFGF levels from samples including serum, plasma, or tissue homogenates. It uses the Sandwich-ELISA mechanism in combination with the enzyme-substrate chromogenic reaction to measure the bFGF content in the sample. The color intensity is positively correlated with the bFGF content in the sample.
FGF2, also called bFGF, plays an important role in the regulation of cell growth and differentiation under physiological and pathological conditions. It is a potent pro-angiogenic factor. Many studies have shown that FGF2-FGFR signaling participates in several biological processes, including embryonic development, tissue regeneration, wound repair, and normal hematopoiesis. FGF2 exerts an important role in the proliferation of hemangioblasts in the early stages of development. It is also implicated in self-renewal, cell survival, and cell adhesion of human embryonic stem cells. Dysregulated FGF2-FGFR signaling has been found in cancer cells and may be involved in the pathogenesis of many kinds of cancer. Upregulation of FGF2 is related to poor prognosis in patients of many cancer types.