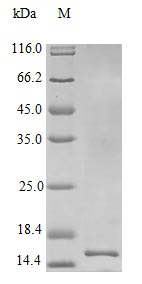
Recombinant Human Interleukin-22 protein (IL22) is produced in an E. coli expression system and contains the complete mature protein sequence from amino acids 34 to 179. This tag-free protein achieves purity levels greater than 97% as verified by SDS-PAGE analysis. The protein demonstrates biological activity with an ED50 of less than 0.3 ng/ml in IL-10 secretion assays using human COLO 205 cells, which translates to a specific activity exceeding 3.3 × 10^6 IU/mg. Endotoxin levels remain below 1.0 EU/µg, making it suitable for research applications.
Interleukin-22 (IL-22) appears to be a cytokine that primarily regulates inflammatory responses while helping maintain epithelial barrier integrity. The protein seems to play a critical role in immune function by influencing pathways involved in tissue repair and pathogen defense. IL-22 has garnered significant research interest due to its involvement in various diseases and potential therapeutic applications for modulating immune responses.
Potential Applications
Note: The applications listed below are based on what we know about this protein's biological functions, published research, and experience from experts in the field. However, we haven't fully tested all of these applications ourselves yet. We'd recommend running some preliminary tests first to make sure they work for your specific research goals.
1. IL-22 Receptor Binding and Signaling Pathway Studies
This recombinant IL-22 protein is confirmed to be biologically active (ED₅₀ < 0.3 ng/ml) and suitable for studying IL-22 receptor binding and downstream signaling. The high specific activity (>3.3×10⁶ IU/mg) and tag-free design ensure reliable dose-response studies of STAT3 phosphorylation and related signaling events. Surface plasmon resonance and other binding assays can accurately determine receptor affinity constants, as the protein's confirmed activity indicates proper folding for receptor engagement.
2. Cytokine-Induced Gene Expression Analysis
The validated biological activity makes this IL-22 protein appropriate for gene expression profiling in IL-22-responsive cells. The demonstrated induction of IL-10 in COLO 205 cells confirms its functionality in regulating gene expression. RNA sequencing or qPCR studies can reliably identify IL-22-responsive genes, particularly in epithelial cells where IL-22 signaling is physiologically relevant. Time-course experiments will accurately map gene expression changes following IL-22 stimulation.
3. Cell Proliferation and Survival Assays
This recombinant IL-22 can be used to examine effects on cell proliferation and survival in IL-22-responsive cell types. The high specific activity allows precise dose-titration experiments, and the low endotoxin level ensures that observed responses are specifically due to IL-22 activity. Standard proliferation assays (MTT, BrdU incorporation) will yield reliable results for quantifying IL-22's effects on cellular growth and viability.
4. Antibody Development and Validation
The high-purity (>97%), tag-free IL-22 protein serves as an excellent immunogen for antibody development and validation. The confirmed biological activity enables functional neutralization assays to test antibody blocking capacity by measuring inhibition of IL-10 induction in COLO 205 cells. This protein is suitable for immunization protocols, ELISA development, and as a positive control in antibody characterization studies.
5. Protein-Protein Interaction Studies
The biologically active, tag-free IL-22 protein is appropriate for interaction studies, including co-immunoprecipitation and pull-down assays to identify binding partners. The confirmed activity indicates proper folding for studying interactions with known IL-22 receptors. However, for novel interaction partners identified through screening assays, validation with mammalian-expressed IL-22 is recommended to account for potential differences in post-translational modifications.
Final Recommendation & Action Plan
This E. coli-expressed Human IL-22 protein is a highly reliable research tool suitable for all proposed applications due to its validated high biological activity, purity, and low endotoxin levels. For immediate use, employ it in IL-22 receptor signaling studies, gene expression analysis, and functional assays using appropriate responsive cell lines. The demonstrated specific activity ensures consistent results across experiments. When developing antibodies, this protein can be used for both immunization and neutralization assays with confidence in its functionality. While the E. coli expression system produces a non-glycosylated form, the confirmed bioactivity indicates proper folding for receptor engagement and biological function. For all applications, include proper controls and dose-response validation to ensure data quality and reproducibility.