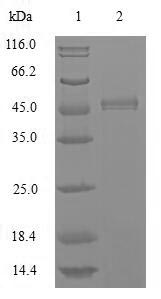
Recombinant Apis mellifera Major royal jelly protein 1 (MRJP1) is produced using a baculovirus expression system, which appears to ensure high-quality protein synthesis. The protein spans the full mature length from amino acids 20-432. It includes an N-terminal 10xHis-tag that makes purification and detection more straightforward. SDS-PAGE analysis confirms purity levels exceeding 85%, suggesting it's well-suited for various research applications.
Major royal jelly protein 1 (MRJP1) represents a key component of royal jelly - that remarkable secretion honeybees use to nourish their larvae and adult queens. The protein likely plays a crucial role in honeybee development and colony dynamics. Given MRJP1's biological functions and its apparent involvement in nutrition and development, it has become an important subject of study in entomology and related fields.
Potential Applications
Note: The applications listed below are based on what we know about this protein's biological functions, published research, and experience from experts in the field. However, we haven't fully tested all of these applications ourselves yet. We'd recommend running some preliminary tests first to make sure they work for your specific research goals.
1. Protein-Protein Interaction Studies Using His-Tag Pull-Down Assays
The utility of this recombinant MRJP1 for interaction studies is critically dependent on its folding state. The baculovirus system increases the probability of proper folding, but this is not guaranteed. If correctly folded, it could identify physiological binding partners, such as other royal jelly proteins or components in honeybee larval food. However, if misfolded, it may yield non-specific (false-positive) or non-physiological interactions, rendering the data unreliable and misleading without independent confirmation of its native structure.
2. Antibody Development and Immunoassay Applications
This protein can serve as an immunogen for antibody development. Even if misfolded, it will generate antibodies against linear epitopes, useful for techniques like Western blotting. However, for producing antibodies that recognize the native conformation of MRJP1 (e.g., for ELISA or immunoprecipitation under non-denaturing conditions), the protein must be correctly folded. Its usefulness for generating conformation-specific antibodies is contingent on its correct folding, which is unknown.
3. Biochemical Characterization and Stability Studies
This application is the primary and essential first step to determine the protein's folding state and biophysical properties. Techniques like Size Exclusion Chromatography (SEC) and Circular Dichroism (CD) can assess its oligomeric state, homogeneity, secondary structure, and thermal stability, providing critical data on whether the protein is natively folded.
4. Comparative Protein Analysis and Evolutionary Studies
This protein can be used for sequence-based comparisons (e.g., as a standard in Western blotting). However, for meaningful comparative structural or functional studies (e.g., comparing stability or ligand binding across species), all proteins being compared must be in their native, correctly folded states. Any functional or structural comparative analysis would be invalid without confirmation of correct folding.
Final Recommendation & Action Plan
The unknown folding state is the critical limiting factor. The only scientifically valid course of action is to prioritize Application 3 (Biochemical Characterization) above all others to determine if the protein is correctly folded. SEC and CD analyses must be performed first. If the protein is folded correctly and is monodisperse, it becomes suitable for Applications 1, 2 (for conformation-specific antibodies), and meaningful comparative studies in Application 4. If it is misfolded or aggregated, its use should be restricted to Application 2 for generating linear epitope antibodies and as a control reagent. Investing in functional studies (Application 1) before this validation is high-risk.