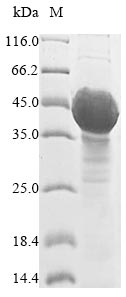
Recombinant Arabidopsis thaliana UDP-glycosyltransferase 89C1 (UGT89C1) is expressed in a yeast system and contains the full-length protein of 435 amino acids. The protein includes an N-terminal 10xHis-tag that makes purification and detection more straightforward. SDS-PAGE analysis shows it reaches a purity above 85%, which should deliver reliable results across different applications. This product is for research use only.
UDP-glycosyltransferase 89C1 (UGT89C1) from Arabidopsis thaliana appears to be involved in glycosylating small molecules, which affects their solubility, stability, and activity in the plant. This enzymatic change likely plays an important role in multiple metabolic pathways and may influence processes like plant defense responses and secondary metabolite production. Studying how UGT89C1 works could help us better understand plant physiology and how plants adapt to their environment.
Potential Applications
Note: The applications listed below are based on what we know about this protein's biological functions, published research, and experience from experts in the field. However, we haven't fully tested all of these applications ourselves yet. We'd recommend running some preliminary tests first to make sure they work for your specific research goals.
Arabidopsis thaliana UGT89C1 is a plant UDP-glycosyltransferase that requires precise folding, proper dimerization, and correct active site formation for its enzymatic activity in glycosylation reactions. The yeast expression system provides a eukaryotic environment that supports proper protein folding and post-translational modifications, increasing the probability of correct folding compared to bacterial systems. However, as a plant-specific enzyme, UGT89C1 may require plant-specific modifications or chaperones for optimal folding. The N-terminal 10xHis tag is relatively small but may potentially interfere with the protein's N-terminal structural organization. While yeast expression provides favorable conditions, experimental validation remains essential to confirm structural integrity and enzymatic activity.
1. Protein-Protein Interaction Studies Using His-Tag Pull-Down Assays
This application requires proper folding validation. Glycosyltransferase interactions within metabolic pathways require precise tertiary structure. If correctly folded (verified), the protein is suitable for identifying physiological interaction partners in plant metabolic networks. If misfolded/unverified, there is a high risk of non-specific binding or failure to identify genuine metabolic pathway interactions.
2. Antibody Development and Validation
Antibody development relies primarily on antigenic sequence recognition. If correctly folded (verified), the protein excels for generating conformation-sensitive antibodies that recognize native UGT89C1 epitopes. If misfolded/unverified, it remains suitable for producing antibodies against linear epitopes, which are still valuable for detection applications in plant research.
3. Biochemical Characterization and Enzyme Kinetics Analysis
These studies are essential for determining folding status and functional competence. If correctly folded (verified), characterization provides reliable data on glycosyltransferase activity, substrate specificity, and kinetic parameters. If misfolded/unverified, analysis yields physical property data, but enzymatic assays will not reflect native activity.
4. Comparative Functional Studies with Other UGT Family Members
This application depends on correct folding validation. Meaningful comparative studies require native protein conformation and enzymatic activity. If correctly folded (verified), the protein enables valid functional comparisons with other UGT family members. If misfolded/unverified, comparative analyses would yield misleading results about evolutionary relationships and functional diversity.
Final Recommendation & Action Plan
The yeast expression system provides favorable folding conditions for this plant glycosyltransferase, but experimental validation of structural integrity and enzymatic activity is essential before reliable use in functional studies. Begin with Application 3 (Biochemical Characterization) to assess folding quality through size-exclusion chromatography (dimerization state), circular dichroism spectroscopy, and validate enzymatic activity using standard UDP-sugar donors and acceptor substrates. If correct folding and enzymatic activity are verified, proceed cautiously with Applications 1 and 4 for interaction studies and comparative functional analyses. Application 2 (antibody development) can proceed immediately regardless of folding status. If misfolding is detected, limit applications to linear epitope antibody production and basic biophysical characterization, avoiding all functional interaction and comparative studies. For reliable UGT89C1 research, always include appropriate enzymatic activity controls and consider using plant-based expression systems for complete plant-specific modifications.