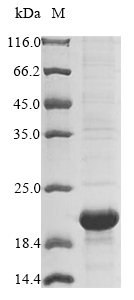
Recombinant Escherichia coli Prophage outer membrane lipoprotein RzoR is produced using an E. coli expression system and carries an N-terminal 6xHis-Flag tag. The protein appears to be expressed as the full length mature form, covering amino acid region 20-61. SDS-PAGE analysis shows the product reaches purity levels above 85%, which should provide reliable results for research applications.
RzoR is a prophage outer membrane lipoprotein found in Escherichia coli, particularly within the K12 strain. It seems to play a role in how phage particles organize structurally, contributing to both stability and assembly of phage components. Studying RzoR may offer insights into bacterial phage biology - research that could prove valuable for understanding microbial genetics and developing phage therapy approaches.
Potential Applications
Note: The applications listed below are based on what we know about this protein's biological functions, published research, and experience from experts in the field. However, we haven't fully tested all of these applications ourselves yet. We'd recommend running some preliminary tests first to make sure they work for your specific research goals.
E. coli RzoR is a prophage-encoded outer membrane lipoprotein that requires precise folding, proper N-terminal lipidation (cysteine acylation with diacylglycerol), membrane integration, and specific tertiary structure for its functional role in prophage-mediated lysis. The standard E. coli expression system cannot provide the essential lipidation machinery required for proper membrane localization and function. While the protein region (20-61aa, 42 amino acids) represents the full-length mature protein after signal peptide cleavage, the lack of lipidation at the N-terminal cysteine (typically Cys20) means the protein cannot form its native structure or function properly. The dual N-terminal 6xHis-Flag tag further disrupts the protein's natural structure and prevents membrane association.
1. Antibody Development and Immunological Studies
This application has severe limitations. While antibodies can be generated, they will primarily target the foreign tags and linear epitopes. Antibodies may not recognize the native, lipidated, membrane-integrated RzoR protein due to the critical structural differences between the lipidated and non-lipidated forms.
2. Structural and Biophysical Characterization
Basic biophysical analysis can be performed but will not reflect native RzoR structure. The lack of lipidation means the protein will adopt a solution structure completely different from the membrane-associated native form. Results will describe an artificial construct rather than the physiological lipoprotein.
3. ELISA-Based Quantitative Assays
This application is feasible for detecting the recombinant RzoR protein, but is biologically irrelevant for native RzoR. Assays will measure the tagged, non-lipidated protein, which has different epitopes and a structure than the native membrane-associated RzoR. Quantitative data will not correlate with physiological RzoR expression.
Final Recommendation & Action Plan
This recombinant RzoR is unsuitable for functional studies despite being the full-length mature protein sequence, because the essential N-terminal lipidation required for lipoprotein function is absent in this expression system. The His-Flag tag replaces the natural lipid anchor at Cys20, creating a soluble protein that cannot integrate into membranes or function in lysis mechanisms. Interaction studies and functional studies should be avoided entirely. For reliable RzoR research, study the natively expressed, lipidated protein in its membrane context using specialized lipoprotein expression systems.