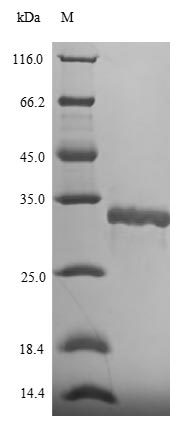
Recombinant Helicobacter pylori DNA protection during starvation protein (dps) is produced in E.coli and contains the complete protein sequence from amino acids 1 to 144. The protein comes with an N-terminal 6xHis-SUMO tag that makes purification and detection more straightforward. SDS-PAGE analysis confirms the product reaches a purity level greater than 90%, which appears suitable for research applications.
The DNA protection during starvation protein (dps) in Helicobacter pylori seems to play a critical role in protecting DNA under oxidative stress and during periods of nutrient deprivation. It's involved in forming a compact nucleoid that may shield DNA from damage. This has made it a significant focus of research in bacterial survival mechanisms and stress responses.
Potential Applications
Note: The applications listed below are based on what we know about this protein's biological functions, published research, and experience from experts in the field. However, we haven't fully tested all of these applications ourselves yet. We'd recommend running some preliminary tests first to make sure they work for your specific research goals.
Helicobacter pylori Dps is a bacterial nucleoid-associated protein that forms dodecameric complexes and requires iron binding for its DNA protection function. The E. coli expression system is generally compatible with bacterial proteins, and the SUMO tag may enhance solubility. However, Dps requires precise oligomerization (12-mer formation) for activity, and the large N-terminal SUMO tag (∼15 kDa) may sterically interfere with proper dodecamer assembly. While the protein may be soluble, the probability of correct oligomerization and functional activity is moderate but requires experimental validation due to potential tag interference.
1. Protein-Protein Interaction Studies Using Pull-Down Assays
The large SUMO tag may sterically hinder interaction interfaces or prevent proper dodecamer formation, leading to non-specific binding or failure to identify genuine partners. If correctly oligomerized, it could reveal physiological interactions, but results require validation with tag-free protein.
2. Antibody Development and Validation
This recombinant Dps serves as an excellent immunogen for generating antibodies against H. pylori Dps. The full-length sequence ensures comprehensive coverage of the epitope. The high purity minimizes antibodies against contaminants. These antibodies will be valuable for detecting Dps in bacterial samples.
3. Biochemical Characterization and Protein Stability Studies
This is the essential first step to assess protein quality. Techniques like size-exclusion chromatography with multi-angle light scattering (SEC-MALS) can determine oligomeric state and confirm dodecamer formation. Circular dichroism can analyze secondary structure, and iron-binding assays can validate functional activity. SUMO protease cleavage allows comparison of tagged vs. untagged protein properties.
4. Comparative Proteomics and Cross-Species Analysis
This protein can be used for sequence-based comparisons and immunological studies. However, functional comparative analyses (e.g., DNA-binding affinity, oxidative stress protection) require proper oligomerization and would be invalid if the tag interferes with dodecamer formation.
Final Recommendation & Action Plan
This recombinant Dps has potential for multiple applications but requires validation of oligomerization and functional activity before reliable use in interaction or comparative functional studies. The immediate priority is Application 3 (Biochemical Characterization) to assess dodecamer formation via SEC-MALS and validate iron-binding/DNA-protection activity. If proper oligomerization is confirmed, proceed with Applications 1 and functional aspects of Application 4. Application 2 (Antibody Development) can proceed immediately. Consider SUMO tag removal for critical functional studies. This systematic approach ensures appropriate use based on functional validation.