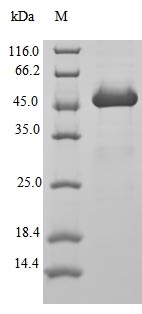
Amino acids 2-181 constitute the expression domain of recombinant Human ARF1. The calculated molecular weight for this ARF1 protein is 55.7 kDa. This ARF1 recombinant protein is manufactured in e.coli. The N-terminal 10xHis-GST tag and C-terminal Myc tag was fused into the coding gene segment of ARF1, making it easier to detect and purify the ARF1 recombinant protein in the later stages of expression and purification.
ADP-ribosylation factor 1 (ARF1) is a critical protein involved in intracellular membrane transport and signal transduction. Some studies indicates that ARF1 plays a crucial role in the highly dynamic endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi apparatus-cell membrane system. Actually, ARF1 stands out for its role in controlling the secretion pathway. As a GTPase, ARF1 controls the formation and fusion of intracellular membrane vesicles by transitioning between active and inactive states on the membrane. This is vital for fundamental cellular processes such as intracellular protein transport, secretion, and endocytosis. In addition, ARF1 is implicated in regulating the dynamic balance of the cell cytoskeleton and cell polarity. It influences the invasion and metastasis of tumor cells and plays a role in synapse formation in neurons.