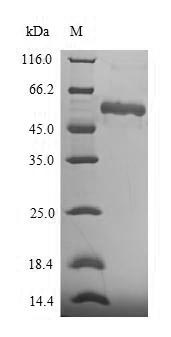
The expression of recombinant human ASPN protein includes the construction of the expression vector containing the recombinant DNA and the transformation of the expression vector into the E.coli, which provides a variety of macromolecules and components required for transcription and translation. The recombinant DNA was formed by fusing the N-terminal 6xHis-SUMO tag sequence to the designated sequence encoding the 33-380aa of the human ASPN protein. This N-terminal 6xHis-SUMO-tagged recombinant human ASPN protein is also characterized by high purity, >90%. Under SDS-PAGE condition, this recombinant ASPN protein migrated to the band of about 55 kDa molecular weight.
It is well-documented that ASPN was upregulated in different stages of gastric cancer (GC),and associated with a poor prognosis and could serve as a potential prognostic biomarker in colorectal cancer. Further data suggested that it promotes the migration and invasion of colorectal cancer cells via TGFβ/Smad2/3 pathway. Asporin as an ECM protein, which belongs to a small leucine-rich proteoglycan family. In ovarian cancinoma, researchers determined that ASPN is highly expressed in CAFs of high grade serous ovarian cancinoma patients and predicts poor prognosis. Moreover, ASPN may be a potential promising biomarker for heart failure. ASPN protein was reported to significantly increased in ischemic cardiomyopathy and dilated cardiomyopathy left ventricular samples. ASPN protein was significantly increased in ICM and DCM left ventricular samples. In additon, asporin levels will be increased as a result of degeneration in advanced TMJ joint disease with tissue damage.