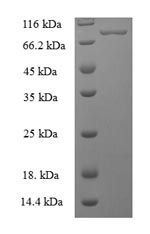
Intact human bifunctional polynucleotide phosphatase/kinase (PNKP) cDNA (1-521aa) with an N-terminal 6xHis-SUMO-tag was expressed in the E.coli. The forming protein is the recombinant full-length human PNKP protein. The purity of this protein is greater than 90% determined by SDS-PAGE. Under reducing conditions, the gel showed a molecular weight band of about 90 kDa. This recombinant PNKP protein may be applied for specific antibody production or in the studies of epigenetics and nuclear signaling.
PNKP is a DNA repair factor possessing both DNA 5’-kinase and DNA 3’-phosphatase activities to modify the ends of a DNA break before ligation. In addition to its role in DNA repair, PNKP plays an important role in normal neurogenesis and also exerts crucial genome maintenance functions after its completion. PNKP mutations are associated with a spectrum of neurodevelopmental disorders, such as microcephaly, seizures, and developmental delay (MCSZ) to ataxia with oculomotor apraxia type 4 (AOA4).