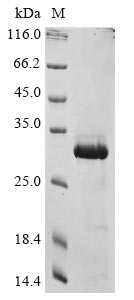
Recombinant Human COMM domain-containing protein 5 (COMMD5) is produced in E.coli and includes the full length of the mature protein, covering amino acids 2 to 224. An N-terminal 6xHis-tag has been added to help with purification and detection. SDS-PAGE analysis shows the protein achieves a purity level greater than 85%. The product is intended for research use only and appears to perform reliably in laboratory settings.
COMMD5 belongs to the COMM domain-containing protein family, which seems to play a role in various cellular processes. The protein is involved in intracellular signaling pathways and may contribute to regulating protein trafficking and degradation. Studying this protein is important for understanding cellular homeostasis and could provide insights into the broader functions of COMM domain-containing proteins in human biology.
Potential Applications
Note: The applications listed below are based on what we know about this protein's biological functions, published research, and experience from experts in the field. However, we haven't fully tested all of these applications ourselves yet. We'd recommend running some preliminary tests first to make sure they work for your specific research goals.
Human COMMD5 is a eukaryotic protein that requires precise folding, proper tertiary structure, and specific domain organization (including the COMM domain) for its functional activity in protein-protein interactions, cytoskeletal regulation, and endosomal trafficking. The E. coli expression system cannot provide the eukaryotic folding environment, chaperones, or post-translational modifications necessary for optimal folding. Although the full-length mature protein (2-224aa) contains all functional domains and the small N-terminal 6xHis-tag may cause minimal steric interference, the probability of correct folding with functional bioactivity is low without experimental validation. COMMD5's known interactions with Rab5, actin, and tubulin require native conformation, which E. coli may not support.
1. Protein-Protein Interaction Studies
This application carries a high risk without functional validation. COMMD5 interactions with partners (e.g., Rab5, cytoskeletal proteins) require precise folding and COMM domain integrity. If correctly folded and active (verified), the protein may identify physiological binders; if misfolded/unverified, pull-down assays may yield tag-mediated artefacts or non-specific binding.
2. Antibody Development and Validation
This application is highly suitable as antibody development relies on antigenic sequence recognition rather than functional folding. The full-length protein provides comprehensive epitope coverage, and high purity (>85%) minimizes cross-reactivity risks.
3. Structural and Biophysical Characterization
These studies are essential for assessing folding status but may not reflect native structure. Techniques like circular dichroism or SEC can evaluate secondary structure and oligomerization, but E. coli-derived protein may lack eukaryotic-specific features (e.g., proper disulfide bonds).
4. Biochemical Assay Development
This application is unsuitable for functional assays without activity validation. COMMD5's role in EGFR trafficking or cytoskeletal coordination requires native conformation. If misfolded, the protein cannot serve as a reliable standard for physiological studies.
Final Recommendation & Action Plan
The E. coli-expressed COMMD5 with a small His-tag may be partially folded but requires rigorous validation before functional use due to the prokaryotic system's inability to support eukaryotic folding mechanisms. Begin with biophysical characterization (Application 3) to assess folding quality via circular dichroism and size-exclusion chromatography. Application 2 (antibody development) can proceed immediately. Applications 1 and 4 should be avoided until functional validation (e.g., Rab5 binding or cytoskeletal interaction assays) confirms bioactivity. For reliable COMMD5 research, use mammalian expression systems (e.g., HEK293) that preserve native structure and interactions .