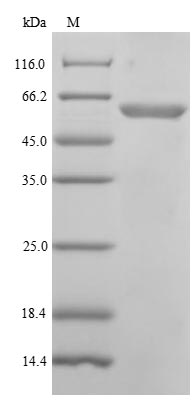
The recombinant Human POLM protein is made through genetic engineering, also called gene splicing or recombinant DNA technology. By putting Human POLM genes into the genetic material of the E.coli system. These microorganisms can be used as factories or producers to make proteins for medical, academic and research uses. DNA to be manipulated it must be placed within a “transport vehicle” in which proteins may be produced from the genetic code of the DNA. The host cells used for Human POLM protein synthesis are E.coli cells, the whole production processes include isolation of POLM gene, amplification of POLM gene, cloning, POLM gene selection, and expression, and the POLM protein purification, the vector contains N-terminal 6xHis tag in addition to the specific DNA sequence, this facilitates the purification of the recombinant protein and it’s finally detected with a purity of 85%+ by SDS-PAGE.
POLM, also called Pol μ, is the only DNA polymerase with template-directed and terminal transferase activities. Pol μ is involved in the gap-filling repair synthesis during the non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) pathway for repair of the DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs). It contributes to the general error-prone bypass of certain kinds of DNA damages like 8-oxo-2′-deoxyguanosine (8-oxodG). Pol μ lacks proofreading activity, with an intrinsically high error rate of 10−3–10−5 for dNTP incorporation. Besides, Pol μ shows a strong preference for manganese over magnesium ions for its terminal deoxynucleotidyltransferase (TdT)-like activity.