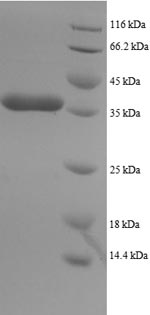
The recombinant Human DYNLL1 protein synthesis in e.coli cells necessitates the incorporation of a DNA fragment encoding the Human DYNLL1 protein (1-89aa) into a plasmid vector, followed by the transformation of this vector into e.coli cells. After screening for positive cells, they are cultured and induced to express the DYNLL1 protein. The protein carries a N-terminal GST tag. Cell lysis is performed to gather the recombinant Human DYNLL1 protein, which undergoes affinity purification and is then analyzed using SDS-PAGE and subsequent staining of the gel with Coomassie Brilliant Blue. The purity of the resulting recombinant Human DYNLL1 protein reaches up to 90%.