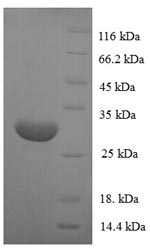
Recombinant Human POU domain class 2-associating factor 1 (POU2AF1) is produced in E. coli and contains the complete protein sequence from amino acids 1-256. The protein includes an N-terminal 6xHis-tag for easier purification and detection. SDS-PAGE analysis shows purity levels above 90%, making it appropriate for research work. This product is strictly for research use only and should not be used for diagnostic or therapeutic purposes.
POU2AF1 appears to play an important role in controlling gene expression within B cells. The protein is known to interact with octamer-binding transcription factors, boosting their activity. It seems to be a key player in transcriptional regulation pathways, which may help researchers better understand immune system processes and how cells differentiate.
Potential Applications
Note: The applications listed below are based on what we know about this protein's biological functions, published research, and experience from experts in the field. However, we haven't fully tested all of these applications ourselves yet. We'd recommend running some preliminary tests first to make sure they work for your specific research goals.
Based on the provided information, the recombinant human POU2AF1 is expressed in E. coli, a prokaryotic system that is generally unsuitable for producing functional eukaryotic transcriptional co-activators. POU2AF1 requires precise folding, specific protein-protein interactions with POU domain transcription factors, and likely post-translational modifications for its co-activator function. While the protein is full-length (1-256aa) with an N-terminal 6xHis tag and >90% purity, E. coli lacks the eukaryotic chaperones and modification machinery necessary for proper folding of complex transcriptional regulators. The N-terminal His-tag may interfere with the native protein structure, particularly if the N-terminus is important for functional interactions. Since activity is unverified, the protein cannot be assumed to be correctly folded or bioactive without experimental validation of its co-activator function and POU domain binding capability.
1. Protein-Protein Interaction Studies Using His-Tag Pull-Down Assays
The N-terminal 6xHis tag enables technical feasibility for pull-down assays, but if POU2AF1 is misfolded (as likely in E. coli), it will not interact physiologically with true binding partners (e.g., POU domain transcription factors). The protein requires precise conformation for specific co-activator interactions. Identified interactions could be non-physiological artifacts. This application should not be pursued without confirmation of proper folding and POU domain binding activity.
2. Antibody Development and Validation
The recombinant POU2AF1 can serve as an effective immunogen for generating antibodies that recognize linear epitopes, even if the protein is misfolded. The full-length sequence ensures broad epitope coverage. However, antibodies may not recognize conformational or modification-dependent epitopes of native, properly folded POU2AF1 in human cells. Validation against endogenous POU2AF1 from mammalian systems is essential.
3. Biochemical Characterization and Stability Studies
This application is well-suited for assessing the recombinant human POU2AF1 itself. Techniques like circular dichroism spectroscopy, size-exclusion chromatography, and thermal shift assays can evaluate the protein's folding state, oligomerization, and stability. These studies are valuable even if the protein is inactive, as they characterize the recombinant human POU2AF1 and can inform about its suitability for other applications.
4. In Vitro Transcription Assays as a Co-activator
This application is highly problematic without activity verification. If POU2AF1 is misfolded, it will not function properly as a transcriptional co-activator in cell-free systems. Transcription assays require precise protein-protein interactions with transcription factors and the basal transcriptional machinery. This application requires prior demonstration of proper folding and co-activator activity with known POU domain partners.
Final Recommendation & Action Plan
Given the high probability of misfolding in E. coli for this complex eukaryotic transcriptional co-activator, we recommend first performing comprehensive validation: 1) Biophysical characterization (circular dichroism for secondary structure, analytical ultracentrifugation for oligomeric state) to assess folding quality; 2) Functional validation of POU domain binding using known interaction partners (e.g., OCT proteins) and co-activator activity in reporter assays; 3) If possible, comparison with POU2AF1 from mammalian expression systems. Antibody development can proceed immediately as the safest application. Avoid all functional studies (interactions, transcription assays) until proper folding and co-activator activity are confirmed. For reliable POU2AF1 functional studies, obtain the protein from mammalian expression systems capable of proper folding and post-translational modifications. Always include appropriate controls, such as known POU domain proteins and validated transcriptional reporters, in experiments.