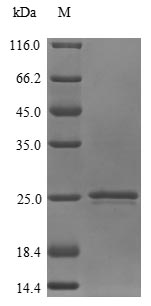
Recombinant Human Prostaglandin E synthase 3 (PTGES3) is produced through a yeast expression system, which appears to deliver high-quality protein expression. This full-length protein covers amino acids 1 to 160 and includes an N-terminal 10xHis-tag that helps with purification and detection. The product shows purity greater than 85% when measured by SDS-PAGE, suggesting it may be suitable for various research applications. However, it's only available for research use, with no claims for diagnostic or therapeutic purposes.
Prostaglandin E synthase 3 (PTGES3) is an enzyme that participates in prostaglandin biosynthesis. Prostaglandins are lipid compounds that play critical roles in inflammation and other physiological processes. PTGES3 seems particularly important for converting prostaglandin H2 to prostaglandin E2 - a molecule with significant implications for immune response regulation and other biological pathways. Understanding this enzyme is likely crucial for grasping how these key processes work in human health and disease.
Potential Applications
Note: The applications listed below are based on what we know about this protein's biological functions, published research, and experience from experts in the field. However, we haven't fully tested all of these applications ourselves yet. We'd recommend running some preliminary tests first to make sure they work for your specific research goals.
Based on the provided information, the recombinant PTGES3 may have a moderate probability of correct folding due to the yeast expression system, which can support eukaryotic-like folding and potential post-translational modifications. However, the N-terminal 10xHis tag, while relatively small, could still sterically interfere with the protein's native structure if it is near functional domains or the active site, potentially affecting bioactivity. The purity of >85% indicates the presence of impurities that might include misfolded or inactive proteins. Without experimental validation (e.g., circular dichroism for secondary structure, enzyme activity tests for prostaglandin E synthase function), it cannot be confirmed that the protein is correctly folded or bioactive. Therefore, the folding status and bioactivity remain uncertain and require verification.
1. Protein-Protein Interaction Studies
The N-terminal 10xHis-tagged PTGES3 can be used in pull-down assays to identify binding partners only if the protein is verified to be correctly folded. If misfolded, interactions may be non-specific or artifactual, leading to false positives/negatives. The His-tag enables immobilization, but the full-length sequence does not guarantee functional binding interfaces. It is recommended to validate folding via biophysical methods before interaction studies to ensure biological relevance.
2. Antibody Development and Validation
This recombinant PTGES3 can serve as an immunogen for antibody generation, but the specificity of antibodies will depend on the protein's folding state. If correctly folded, antibodies may recognize native epitopes; if misfolded, they could target non-conformational epitopes, reducing utility for detecting physiological PTGES3. The His-tag aids in purification and assay development, but cross-reactivity with the tag should be controlled. Folding validation is advised for reliable antibody outcomes.
3. Biochemical Characterization and Enzyme Assays
The purified PTGES3 is suitable for biochemical studies only if correctly folded and functional. Enzyme assays require active protein; if misfolded, activity measurements will be invalid. Thermal stability and folding studies can be performed, but results must be interpreted cautiously without prior validation. The yeast system may support folding, but enzymatic activity tests (e.g., prostaglandin E2 synthesis assays) are essential to confirm bioactivity before detailed characterization.
4. His-Tag Affinity Purification Method Development
This His-tagged PTGES3 is appropriate for developing purification protocols, as this application is independent of protein folding or bioactivity. The tag allows optimization of nickel-affinity conditions, elution strategies, and yield assessment. However, for biological use, the purified protein should undergo folding validation to ensure it meets functional standards.
Final Recommendation & Action Plan
To ensure reliable results, first validate the folding and bioactivity of the recombinant PTGES3 using techniques such as circular dichroism to assess secondary structure, size-exclusion chromatography for oligomeric state, and enzyme activity assays (e.g., measuring prostaglandin E2 production) to confirm functionality. If validation fails, consider using a tag-cleaved protein or alternative sources for functional studies. For applications like antibody development or purification optimization, the protein can be used directly with controls for folding-related artifacts, but critical biochemical or interaction studies should await confirmation of correct folding.