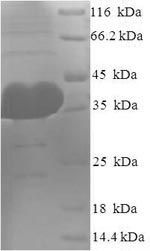
Amino acids 517-818 constitute the expression domain of recombinant Human AGO2. This AGO2 protein is expected to have a theoretical molecular weight of 38.1 kDa. Expression of this AGO2 protein is conducted in e.coli. The N-terminal 6xHis tag was fused into the coding gene segment of AGO2, making it easier to detect and purify the AGO2 recombinant protein in the later stages of expression and purification.
The human protein argonaute-2 (AGO2) is a key component of the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC) and a member of the Argonaute protein family. AGO2 plays a central role in RNA interference (RNAi) and microRNA (miRNA) pathways. AGO2 is involved in post-transcriptional gene regulation by binding to small RNA molecules, such as miRNAs and small interfering RNAs (siRNAs). This binding allows AGO2 to guide RISC to complementary mRNA sequences, leading to mRNA cleavage or translational repression. AGO2 is essential for processes like gene silencing, antiviral defense, and maintaining genome stability. Research on AGO2 explores its intricate functions in RNA silencing pathways and its potential applications in therapeutic interventions.