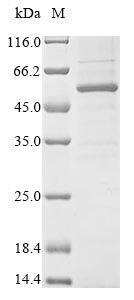
Recombinant Mouse Chordin-like protein 1 (Chrdl1) is produced through a baculovirus expression system, spanning the full length of the mature protein from amino acids 23 to 447. The protein includes an N-terminal 10xHis tag and a C-terminal Myc tag, which makes purification and detection more straightforward. SDS-PAGE analysis confirms the protein achieves greater than 85% purity, though this may vary slightly between batches depending on expression conditions.
Chordin-like protein 1 (Chrdl1) appears to play an important role in controlling signaling pathways during embryonic development and tissue homeostasis. Current research suggests it regulates various growth factors, which likely influence how cells differentiate and multiply. This makes Chrdl1 particularly interesting for developmental biology studies, though our understanding of its complete regulatory network remains incomplete.
Potential Applications
Note: The applications listed below are based on what we know about this protein's biological functions, published research, and experience from experts in the field. However, we haven't fully tested all of these applications ourselves yet. We'd recommend running some preliminary tests first to make sure they work for your specific research goals.
The baculovirus expression system provides proper eukaryotic folding machinery and can perform complex post-translational modifications, significantly increasing the likelihood that this mouse Chrdl1 protein will achieve correct folding. As a secreted glycoprotein involved in BMP signaling inhibition, Chrdl1 requires proper disulfide bond formation and glycosylation for its biological activity. While the baculovirus system is superior to bacterial systems for such proteins, the actual folding status and functional activity cannot be guaranteed without experimental validation. The presence of dual tags, particularly the C-terminal Myc tag, may potentially interfere with the protein's C-terminal structure or function.
1. Antibody Development and Validation
This recombinant Chrdl1 serves as an excellent immunogen for generating specific antibodies. The full-length mature protein sequence ensures comprehensive epitope coverage, and the baculovirus expression system likely produces properly folded protein with correct conformational epitopes. The dual tags provide flexible options for purification and screening. The resulting antibodies will be valuable for detecting Chrdl1 in mouse tissues and studying its expression patterns.
2. Protein-Protein Interaction Studies
This application carries significant risk without folding validation. If correctly folded, the protein could identify physiological binding partners like BMPs or related receptors. However, if misfolded or if the tags interfere with binding interfaces, it may yield non-specific interactions or fail to recognize genuine partners, making data interpretation problematic. Folding validation is strongly recommended before this application.
3. ELISA-Based Binding Assays
This mouse Chrdl1 protein is well-suited as a standard for quantitative ELISA assays to measure Chrdl1 levels in biological samples. However, for functional binding studies (e.g., measuring BMP binding affinity), the protein must be correctly folded and active. The dual tags provide excellent handles for assay development but may affect functional binding sites. As an immunoassay standard, it's highly suitable. For functional binding studies, it requires prior validation of correct folding and activity.
4. Biochemical Characterization Studies
This application is essential for determining the protein's physical properties and folding status. Techniques like size-exclusion chromatography with multi-angle light scattering (SEC-MALS) can assess oligomeric state and homogeneity, while circular dichroism can analyze secondary structure content and thermal stability. These studies provide critical data on protein folding quality and stability, which determines suitability for functional applications.
Final Recommendation & Action Plan
Given the unknown folding status and potential tag interference, a systematic validation approach is essential. The immediate priority should be Application 4 (Biochemical Characterization) to assess protein folding quality through SEC-MALS and circular dichroism. If the protein demonstrates proper monodisperse folding, a functional assay (e.g., BMP binding inhibition) should be conducted to confirm biological activity. Only after confirming proper folding and activity should the protein be used for Applications 2 and 3 (functional studies). Meanwhile, Application 1 (Antibody Development) can proceed immediately as it doesn't require functional validation. For future studies, consider producing a tag-free version using tag cleavage to eliminate potential tag interference with functional domains.