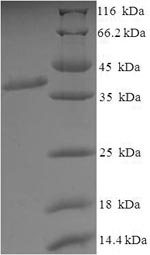
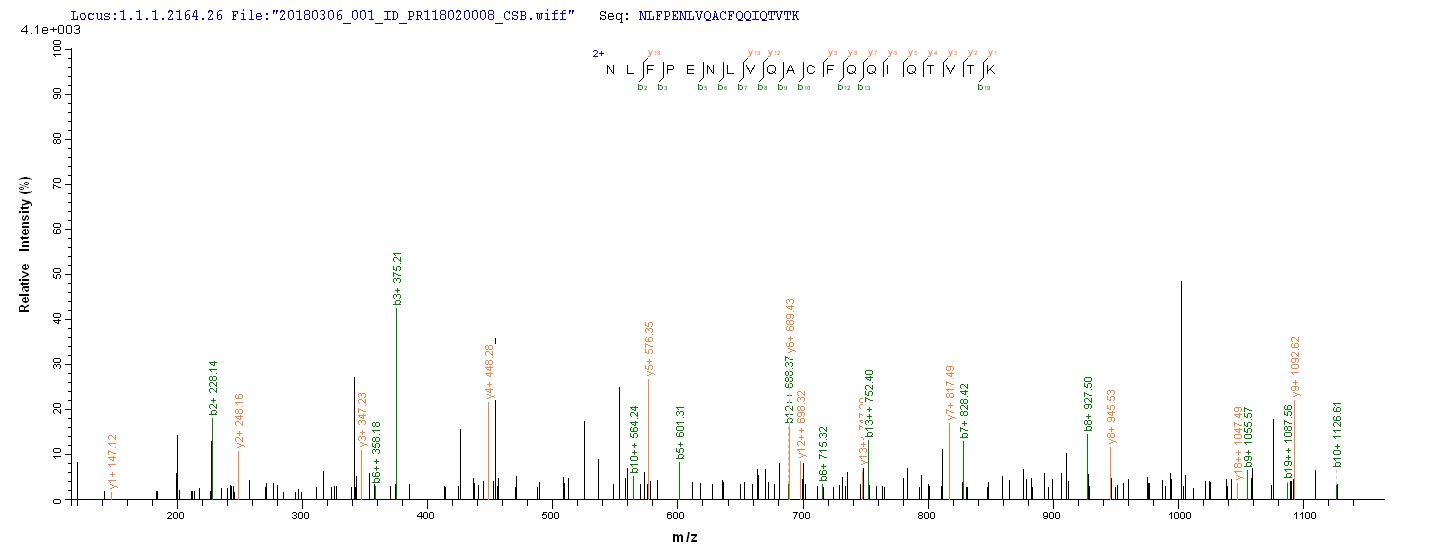
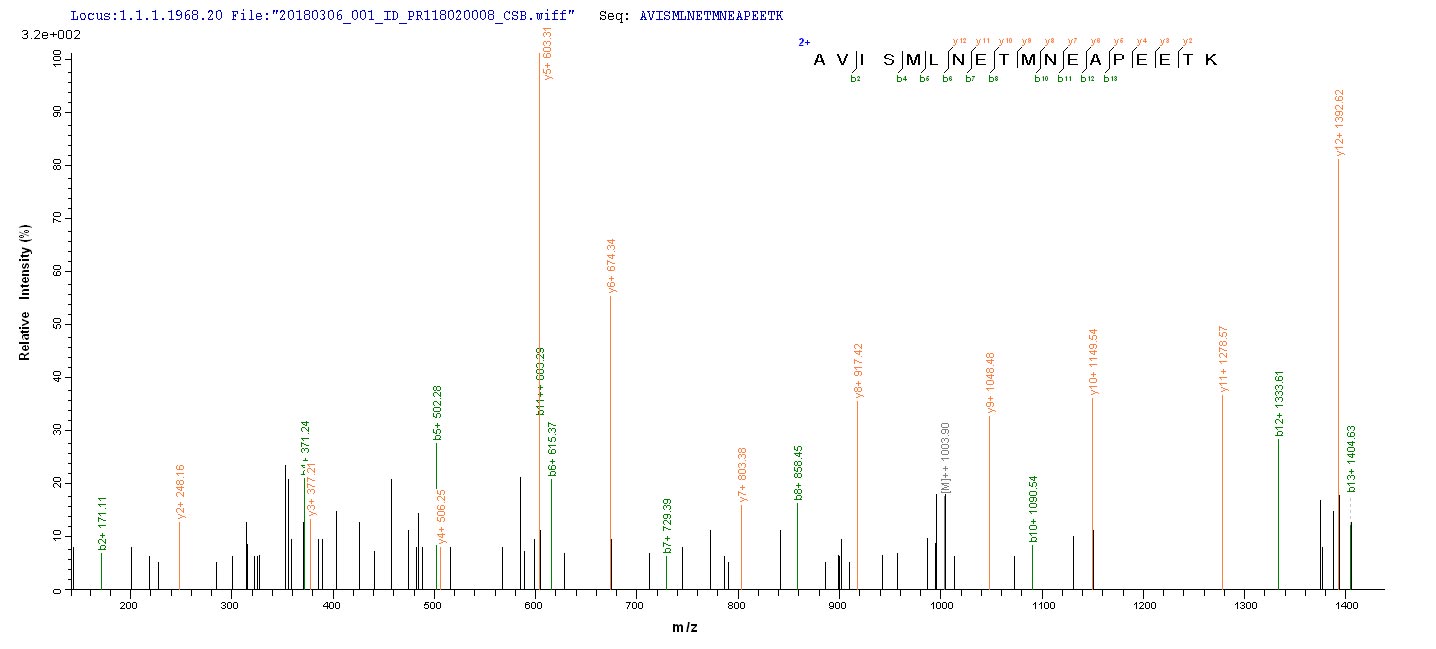
Purity
Greater than 90% as determined by SDS-PAGE.
Alternative Names
Slc1a2; Eaat2; Glt1Excitatory amino acid transporter 2; GLT-1; Sodium-dependent glutamate/aspartate transporter 2; Solute carrier family 1 member 2
Species
Mus musculus (Mouse)
Expression Region
143-238aa
Target Protein
Sequence
HPGNPKLKKQLGPGKKNDEVSSLDAFLDLIRNLFPENLVQACFQQIQTVTKKVLVAPPSEEANTTKAVISMLNETMNEAPEETKIVIKKGLEFKDG
Note: The complete
sequence may include tag sequence, target protein sequence, linker sequence and extra sequence that is
translated with the protein sequence for the purpose(s) of secretion, stability, solubility, etc.
If the exact amino acid sequence of this recombinant protein is critical to your application,
please explicitly request the full and complete sequence of this protein before ordering.
Tag Info
N-terminal GST-tagged
Form
Liquid or Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that
we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your
requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand.
Buffer
If the delivery form is liquid, the default storage buffer is Tris/PBS-based buffer, 5%-50% glycerol.
Note: If you have any special requirement for the
glycerol content, please remark when you place the order.
If the delivery form is lyophilized powder, the buffer before lyophilization is Tris/PBS-based buffer,
6% Trehalose.
Reconstitution
We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20°C/-80°C. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
Storage Condition
Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid
repeated freeze-thaw
cycles.
Shelf Life
The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage
temperature
and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized
form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C.
Lead Time
3-7 business days
Notes
Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
Datasheet & COA
Please contact us to get it.