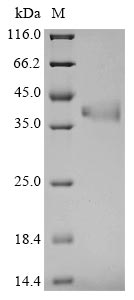
Recombinant Mouse Fructose-bisphosphate aldolase C (Aldoc) is expressed in yeast and contains the complete mature protein sequence, spanning amino acids 2-363. The protein includes a C-terminal 6xHis tag that simplifies purification and detection processes. SDS-PAGE analysis confirms the purity exceeds 90%, which appears to provide reliable results for research applications. The recombinant protein comes with low endotoxin levels, making it appropriate for sensitive experimental work.
Fructose-bisphosphate aldolase C serves as a key enzyme in the glycolytic pathway. It catalyzes the reversible conversion of fructose-1,6-bisphosphate to glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate and dihydroxyacetone phosphate. The enzyme is mainly found in the central nervous system, where it likely plays an important role in energy metabolism within neuronal cells. This makes it particularly interesting for studies focused on metabolic processes and neurological research.
Potential Applications
Note: The applications listed below are based on what we know about this protein's biological functions, published research, and experience from experts in the field. However, we haven't fully tested all of these applications ourselves yet. We'd recommend running some preliminary tests first to make sure they work for your specific research goals.
While the Yeast expression system is advantageous for producing eukaryotic proteins due to its ability to perform certain post-translational modifications and support disulfide bond formation—increasing the probability of proper folding compared to prokaryotic systems like E. coli—this does not guarantee native conformation or bioactivity. Aldolase C is a functional enzyme that requires precise folding into its active tetrameric structure for catalytic activity, which involves cleaving fructose-1,6-bisphosphate into dihydroxyacetone phosphate and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate. The presence of a C-terminal tag, though less likely to interfere with the active site than an N-terminal tag, could still potentially affect oligomerization or functional interactions. Without evidence from biophysical analyses (e.g., circular dichroism, size-exclusion chromatography) or enzymatic assays, the protein’s folding and bioactivity remain unconfirmed.
1. Biochemical Characterization of Aldolase C Enzymatic Properties
This recombinant Aldoc protein could be used to study enzymatic kinetics and substrate specificity only if its folding and bioactivity are experimentally verified. The yeast expression system and full-length design are favorable, but the C-terminal tag might subtly influence oligomerization or kinetics. Without validation (e.g., activity assays measuring fructose-1,6-bisphosphate cleavage), kinetic parameters may be inaccurate. Comparative studies with aldolase A or B isoforms should first confirm that the recombinant protein’s specific activity aligns with native Aldoc behavior.
2. Antibody Development and Validation Studies
The full-length, high-purity protein is suitable as an immunogen for generating antibodies targeting linear epitopes, regardless of folding. However, if the protein is misfolded, antibodies may not recognize conformational epitopes of native Aldoc, limiting the utility of techniques like immunofluorescence that depend on native structure. The His tag facilitates purification but could induce tag-specific antibodies; screening should prioritize clones binding to untagged Aldoc.
3. Protein-Protein Interaction Studies
The His-tagged protein is technically suitable for pull-down assays, but its effectiveness hinges on correct folding. Misfolding could alter interaction interfaces, leading to false negatives (e.g., missing partners like metabolic enzymes or signaling proteins) or non-physiological bindings. Identified interactions must be validated with native Aldoc from brain tissues, where Aldoc is naturally abundant.
4. Structural and Biophysical Analysis
The protein’s suitability for structural studies (e.g., X-ray crystallography) is strictly dependent on proper folding and homogenous oligomerization. Yeast expression may support tetramer formation, but tag presence could disrupt quaternary structure. Biophysical validation (e.g., size-exclusion chromatography for tetrameric state, circular dichroism for secondary structure) is a prerequisite. Misfolded or aggregated protein would yield misleading structural data.
5. Metabolic Pathway Reconstitution Assays
This application is fully contingent on bioactivity confirmation. Aldoc’s role in glycolysis requires precise enzymatic activity for meaningful pathway reconstitution. If inactive, the protein would disrupt metabolic flux measurements in vitro. Activity must be verified spectrophotometrically before integration into multi-enzyme systems; otherwise, results could misrepresent Aldoc’s metabolic contribution.
Final Recommendation & Action Plan
To ensure reliable outcomes, prioritize experimental validation of the protein’s folding and bioactivity before application. Start with biophysical characterization (e.g., size-exclusion chromatography with multi-angle light scattering to assess tetrameric state, circular dichroism for secondary structure) to evaluate structural integrity. Proceed to functional assays using standard enzymatic methods—e.g., spectrophotometric measurement of fructose-1,6-bisphosphate cleavage—and compare kinetics to literature values for native Aldoc. If validated, the protein can confidently be used for the proposed applications; if misfolded/inactive, limit use to non-functional studies like linear-epitope antibody production. Always disclose validation status in reporting to avoid misinterpretation.