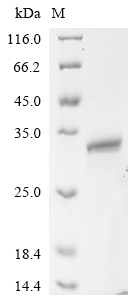
Recombinant Mouse Heme-binding protein 1 (Hebp1) comes from an E.coli expression system and spans the complete protein sequence from amino acids 1 to 190. The construct includes an N-terminal 10xHis tag and a C-terminal Myc tag, which makes purification and detection more straightforward. SDS-PAGE analysis confirms the product achieves greater than 90% purity - a level that appears suitable for most research needs.
Heme-binding protein 1 (Hebp1) binds heme, though the full scope of this interaction remains an active area of investigation. This protein likely contributes to heme metabolism and may play a part in how cells respond to oxidative stress. Scientists are working to better understand Hebp1's role in these pathways, along with its broader involvement in heme-related cellular processes.
Potential Applications
Note: The applications listed below are based on what we know about this protein's biological functions, published research, and experience from experts in the field. However, we haven't fully tested all of these applications ourselves yet. We'd recommend running some preliminary tests first to make sure they work for your specific research goals.
Mouse Hebp1 is a eukaryotic heme-binding protein that requires precise folding and proper heme-binding domain formation for its functional activity. The E. coli expression system cannot provide the necessary eukaryotic folding environment, post-translational modifications, and molecular chaperones required for this protein. While the protein may be soluble, the dual N-terminal 10xHis-tag and C-terminal Myc-tag may sterically interfere with the protein's functional domains.
1. Antibody Development and Validation Studies
This application is highly suitable as antibody development relies on antigenic sequence recognition rather than functional folding. If correctly folded (verified), the protein excels for generating conformation-sensitive antibodies. If misfolded/unverified, it remains highly suitable for producing antibodies against linear epitopes.
2. Tag-Assisted Purification and Detection Assays
This application is well-suited regardless of folding status. Tag-based systems rely on tag functionality rather than native protein folding. The dual tags provide excellent flexibility for purification and detection method development.
3. Biochemical Characterization and Stability Studies
These studies are essential for determining folding status. If correctly folded (verified), characterization provides reliable data on structural properties. If misfolded/unverified, analysis yields physical property data for quality control.
Final Recommendation & Action Plan
The E. coli expression system is fundamentally limited for this eukaryotic protein due to folding environment differences. Begin with Application 3 (Biochemical Characterization) to assess folding quality through techniques like circular dichroism spectroscopy and size-exclusion chromatography. Applications 1 and 2 (antibody development and tag-based assays) can proceed immediately as they don't require native folding. Protein-protein interactions require a precise tertiary structure that E. coli may not provide. If misfolding is detected, limit applications to linear epitope antibody production and tag-based method development.