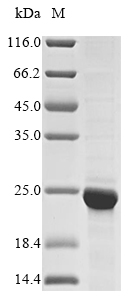
Recombinant Mouse Histone H2B type 1-A (Hist1h2ba) is expressed in E.coli and covers the full length of the mature protein (2-127aa). The construct includes an N-terminal 10xHis tag and a C-terminal Myc tag, which help with purification and detection. SDS-PAGE analysis shows the protein reaches greater than 85% purity, suggesting it's well-suited for research work.
Histone H2B appears to be a core component of the nucleosome and likely plays an important role in how chromatin gets organized and compacted inside the cell nucleus. The protein participates in nucleosome formation - something that seems fundamental to DNA packaging and regulation. Research involving chromatin dynamics, gene expression control, and epigenetic changes often relies on this protein, since understanding these cellular processes at the molecular level may require it.
Potential Applications
Note: The applications listed below are based on what we know about this protein's biological functions, published research, and experience from experts in the field. However, we haven't fully tested all of these applications ourselves yet. We'd recommend running some preliminary tests first to make sure they work for your specific research goals.
The mouse Histone H2B is a core histone that requires correct folding and specific interactions with other histones (H2A, H3, H4) and DNA to form functional nucleosomes. While E. coli can express histones, the dual tags at both termini may interfere with native folding and assembly, as the N- and C-terminal regions of H2B are critical for histone-histone interactions and nucleosome stability. The tags could sterically hinder proper dimerization with H2A or integration into the histone octamer. Although histones are generally stable proteins, the presence of tags and the lack of eukaryotic post-translational modifications (e.g., acetylation) may affect bioactivity. Without experimental validation (e.g., nucleosome reconstitution assays or circular dichroism), it is uncertain whether the protein is correctly folded or bioactive. Therefore, correct folding and bioactivity cannot be assumed and must be verified.
1. Chromatin Reconstitution and Nucleosome Assembly Studies
If the recombinant H2B is verified to fold and assemble correctly with other histones (e.g., through nucleosome reconstitution assays), it can be used for chromatin studies. However, the dual tags may disrupt histone-histone interactions or DNA binding, leading to inefficient nucleosome formation. Results should be validated with tag-free histones to ensure physiological relevance. The tags facilitate purification but may introduce artifacts.
2. Histone-Protein Interaction Studies
This recombinant H2B may be used in pull-down assays to identify binding partners, leveraging the tags for immobilization and detection. However, misfolding or tag-mediated non-specific binding could yield false positives/negatives. Interactions identified must be confirmed with native H2B (e.g., from eukaryotic sources) to ensure they reflect physiological associations.
3. Antibody Development and Validation
This recombinant H2B can serve as an immunogen for antibody production, as antibodies often recognize linear epitopes. The high purity supports consistent immunization and screening. However, antibodies generated may not bind to native H2B in chromatin due to conformational changes caused by tags or misfolding. Validation against tag-free, native H2B is essential for applications like immunofluorescence or ChIP.
4. Biochemical Characterization and Structural Studies
The protein is suitable for basic biophysical analyses (e.g., circular dichroism to assess secondary structure, dynamic light scattering to monitor aggregation). However, for high-resolution structural studies (e.g., X-ray crystallography), the tags may interfere with crystal formation or native conformation. Tag removal is recommended for meaningful structural insights. These assays can help evaluate folding status but not guarantee native structure.
Final Recommendation & Action Plan
Before using this recombinant H2B for functional applications, validate its folding and assembly capability through biophysical and functional tests. Start with circular dichroism to check for expected α-helical content, and perform nucleosome reconstitution assays with other core histones to confirm it can form stable complexes. If activity is verified, proceed with interaction or structural studies; otherwise, limit use to non-functional applications like antibody production, but always validate outcomes with native H2B. For reliable chromatin studies, consider using tag-free histones expressed in eukaryotic systems or cleaving the tags enzymatically. Avoid assumptions about bioactivity without experimental confirmation.