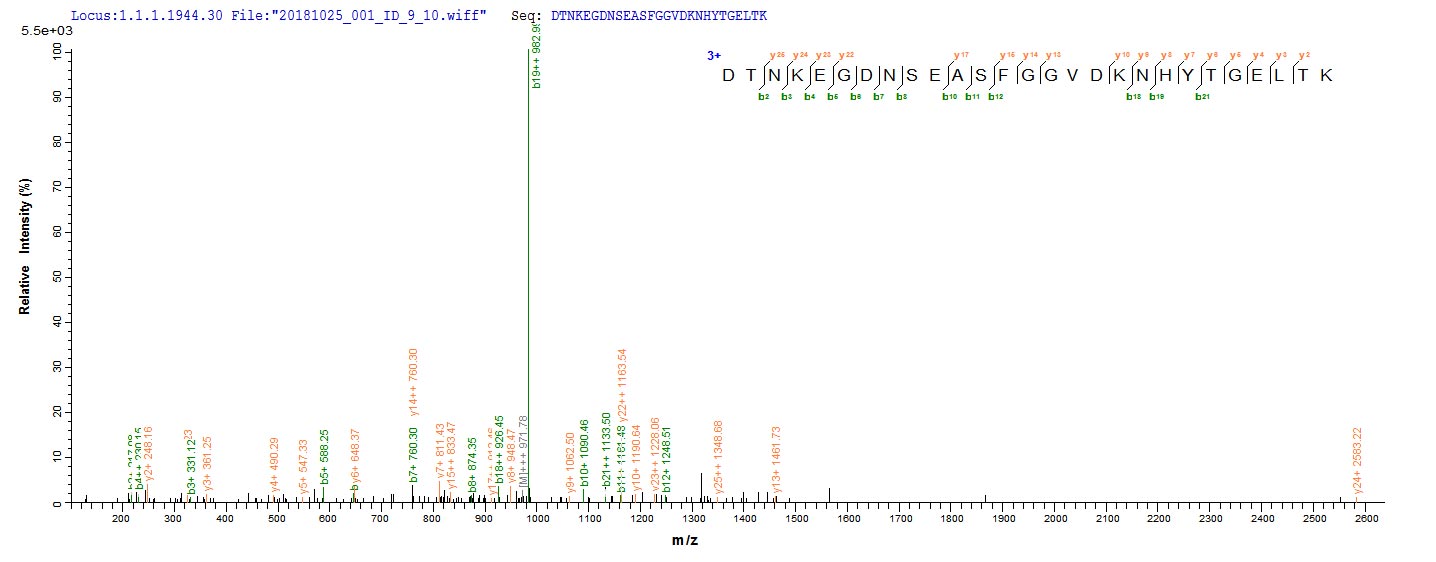
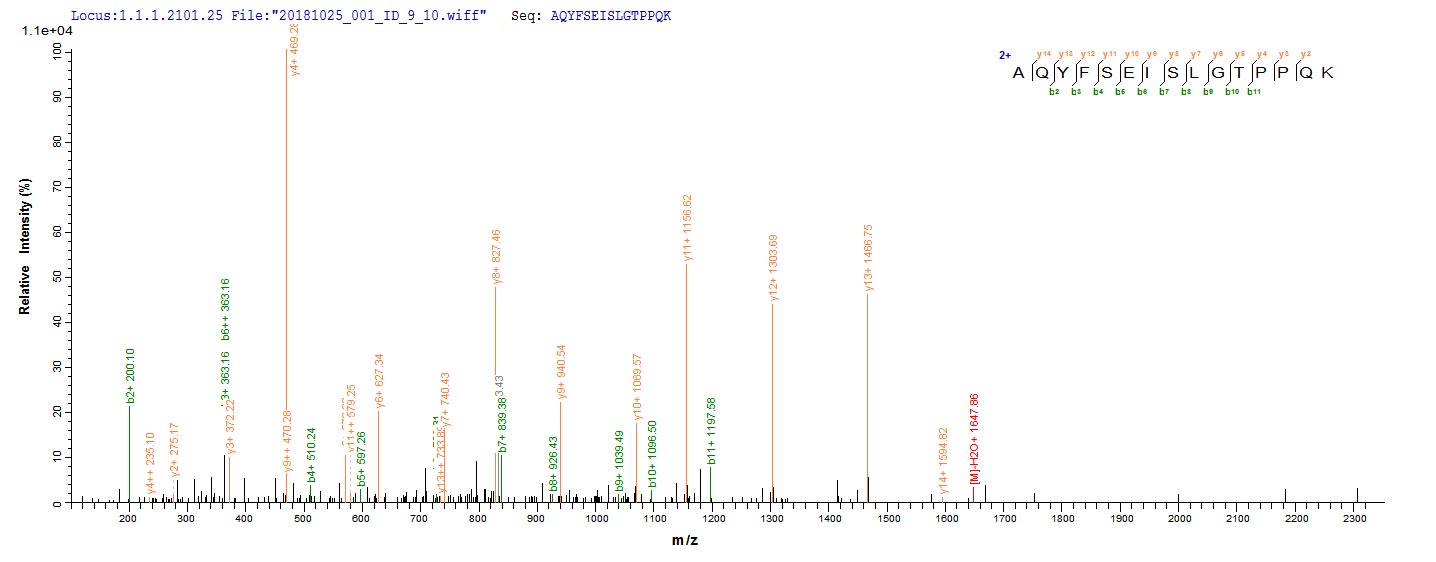
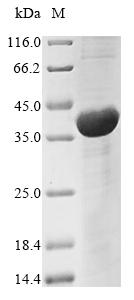
Recombinant Neosartorya fumigata Vacuolar protease A (pep2) is expressed in E.coli, covering the mature protein region from amino acids 71 to 398. This product features an N-terminal 6xHis-tag, which makes purification and detection more straightforward. The protein achieves a purity level greater than 85% as confirmed by SDS-PAGE analysis. It is intended for research use only, without specified endotoxin levels or activity data.
Vacuolar protease A appears to be an important enzyme involved in protein processing and turnover within the fungal vacuole. It likely plays a critical role in the degradation of misfolded or damaged proteins, contributing to cellular homeostasis. Research on this protease may help scientists understand fungal biology better and could provide insights into proteolytic pathways relevant to broader biological systems.
Potential Applications
Note: The applications listed below are based on what we know about this protein's biological functions, published research, and experience from experts in the field. However, we haven't fully tested all of these applications ourselves yet. We'd recommend running some preliminary tests first to make sure they work for your specific research goals.
Based on the provided information, the recombinant protein is produced in an E. coli expression system, while the source protein from Neosartorya fumigata (a fungus, eukaryote) may require eukaryotic-specific post-translational modifications (such as glycosylation, disulfide bond formation, or propeptide activation) for proper folding and bioactivity. E. coli, a prokaryotic system, lacks these modification mechanisms, making the probability of correct folding low. No enzyme activity assays or folding validation data (e.g., circular dichroism, fluorescence spectroscopy, or activity tests) are provided. Therefore, it cannot be confirmed that the protein is correctly folded or bioactive. The protein may be partially denatured or inactive, and validation is essential before any application.
1. Biochemical Characterization of Fungal Vacuolar Protease Activity
Activity assays depend on native folding; unverified proteins risk false negatives/positives due to E. coli's inability to support eukaryotic protein conformations. If the recombinant N. fumigata vacuolar protease A is correctly folded and exhibits protease activity, it can be used to establish in vitro protease activity assays using fluorogenic or chromogenic peptide substrates. Researchers could determine optimal pH, temperature stability, and kinetic parameters to study its biochemical properties, but this requires prior validation of enzyme activity. The N-terminal 6xHis tag facilitates purification and immobilization for kinetics studies. However, if the protein is misfolded or inactive, such assays would yield inaccurate results and should not be attempted without refolding or using an alternative expression system.
2. Antifungal Drug Target Validation Studies
Inhibitor screening relies on enzymatic activity; inactive proteins cannot accurately reflect inhibition. If properly folded and functional, this recombinant protein could serve as a tool for screening protease inhibitors as antifungal compounds in preclinical research. High-throughput screening assays could identify small molecule inhibitors, but only after confirming protease activity. The purified protein enables structure-activity relationship studies and specificity assessments against fungal vs. human proteases. If inactive, these applications would be invalid and could mislead drug development efforts.
3. Antibody Development and Immunological Studies
Immunogenicity doesn’t strictly require correct folding, but antibody specificity may be compromised; denatured proteins as controls risk false positives. The 6xHis-tagged recombinant protein can be used as an immunogen for generating polyclonal or monoclonal antibodies, even if misfolded, as antibodies may recognize linear epitopes. However, antibodies against a misfolded protein might not bind the native protein in fungal cells, limiting utility for localization/functional studies. As a positive control in Western blotting, ELISA, or immunofluorescence, the protein could be used, but results may be unreliable if denatured, and cross-validation with native protein is recommended.
4. Protein-Protein Interaction Studies
Protein interactions depend on 3D structure; misfolding disrupts binding interfaces, invalidating results. If correctly folded, the N-terminal 6xHis tag allows pull-down assays to identify interacting partners from fungal cell lysates via mass spectrometry. However, if misfolded, interaction domains may be altered, leading to false positives/negatives. This approach should only be used after verifying native conformation (e.g., by circular dichroism or activity assays).
5. Comparative Protease Studies Across Fungal Species
Comparative studies demand functional activity; inactive proteins introduce artifacts. If the recombinant protease is active and properly folded, it can serve as a reference for comparative studies with homologous proteases from other fungi, analyzing evolution, substrate preferences, and enzymatic properties. However, if misfolded, comparative data would be biased and not reflect biological differences, requiring activity confirmation prior to use.
Final Recommendation & Action Plan
It is critically recommended to validate the folding and bioactivity of this recombinant protein before any application, as the E. coli expression system may not support proper folding of this eukaryotic protein. The action plan should include: first, performing enzyme activity assays (e.g., using fluorogenic substrates) and folding analysis (e.g., circular dichroism or size-exclusion chromatography); if inactive, consider re-expressing the protein in a eukaryotic system (e.g., yeast or insect cells) or using a commercially available active protein as a control; until validation, all applications should be considered high-risk and avoided in critical experiments to prevent data misinterpretation.