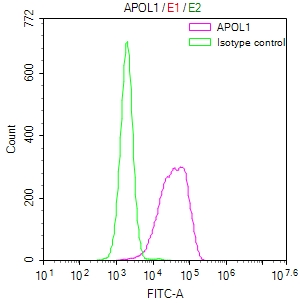
The APOL1 recombinant monoclonal antibody is generated through in vitro processes using synthetic genes. This methodology involves the retrieval of APOL1 antibody genes from B cells sourced from immunoreactive rabbits, followed by their amplification and cloning into appropriate phage vectors. These vectors are then introduced into mammalian cell lines, enabling the production of functional antibodies in substantial quantities. Subsequently, the APOL1 recombinant monoclonal antibody is purified from the culture supernatant of the transfected cell lines through affinity chromatography. It is recommended for the detection of human APOL1 protein in ELISA and FC applications.
APOL1 is a member of the apolipoprotein family and is primarily found in the bloodstream. The main role of APOL1 is to provide protection against African trypanosomes by participating in the innate immune response. Its lytic activity, when functioning effectively, helps to control trypanosome infections.