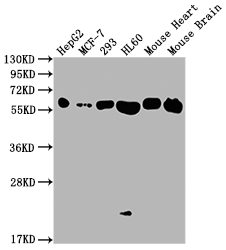
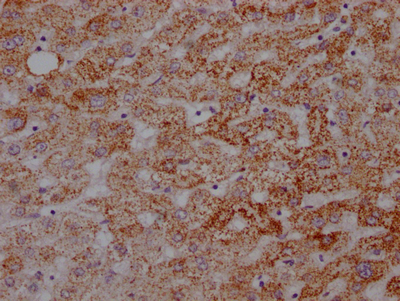
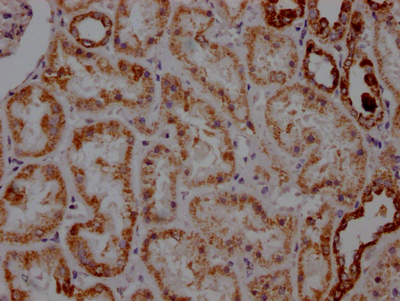
The ATP5A1 recombinant monoclonal antibody can effectively detect human and mouse ATP5A1 proteins in ELISA, WB, and IHC assays. Its production involves recombinant DNA technology, whereby the gene coding for the ATP5A1 monoclonal antibody is synthesized through cDNA sequencing of the ATP5A1 antibody-producing hybridomas. These hybridomas are formed by fusing myeloma cells with B cells derived from animals immunized with a synthesized peptide derived from human ATP5A1. The synthesized gene is then cloned into a vector and then transfected into cells for cultivation. Finally, the ATP5A1 recombinant monoclonal antibody is purified through affinity chromatography from the cell culture supernatant.
ATP5A1 is a subunit of ATP synthase, an enzyme that plays a key role in cellular energy metabolism by synthesizing ATP. Specifically, ATP5A1 is part of the F1 sector of ATP synthase, which catalyzes the ATP synthesis from ADP and inorganic phosphate using energy from the proton motive force across the mitochondrial inner membrane. ATP5A1 contributes to the formation of the catalytic core of the F1 sector and is involved in the binding and hydrolysis of ATP during the reaction cycle of ATP synthase. It is also implicated in several non-metabolic processes, such as cell proliferation and differentiation, apoptosis, and tumorigenesis.