STAG2 encodes a subunit of the cohesin complex and is one of the most mutated genes in human cancer. STAG2 inactivation has been demonstrated to cause aneuploidy via sister chromatid cohesion, as well as increased DNA damage, which could facilitate further mutagenesis. STAG2 is required for the progression of DNA replication forks. STAG2 deficiency disrupts the interaction of cohesin with the replication machinery, resulting in replication fork stalling and collapse, as well as failure to develop SMC3 acetylation. As a result, STAG2 loss causes synthetic lethality with particular DNA repair genes as well as increased chemotherapeutic susceptibility.
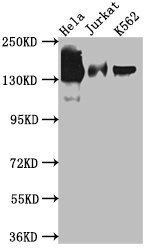
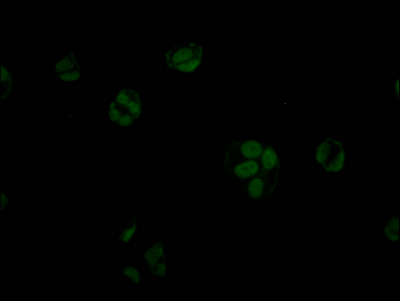
CUSABIO cloned STAG2 antibody-coding genes into plasma vectors and then transfected these vector clones into mammalian cells using a lipid-based transfection reagent. Following transient expression, the recombinant antibodies against STAG2 were harvested and characterized. The recombinant STAG2 antibody was purified by Affinity-chromatography from the culture medium. It can be used to detect STAG2 protein from Human in the ELISA, WB, IF.