Thank you for your continuous support to CUSABIO! In the April, 2024, CUSABIO products published more than 300 articles with a cumulative impact factor of 1500+! The total number of articles has reached 23,600! Thank you for choosing CUSABIO reagent during your scientific research journey. Thank you again for your trust and support. We will continue to work hard to provide you with better products and services! Now let's share our wonderful research results~
CUSABIO Monthly Citations Review
01 An intelligent DNA nanodevice for precision thrombolysis
Impact Factor: 41.2
Journal Name: Nature materials
CUSABIO Citation Product:
CSB-E12984r: Rat D-Dimer,D2D ELISA Kit
Research Highlights:
This article introduces an intelligent drug delivery platform based on DNA nanotechnology, designed with an accurate tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) loading system. By integrating DNA nanosheets and responsive DNA lock structures, it achieves precise identification of thrombin concentration in thrombi and on-demand release of tPA. This DNA nano-device has shown significant improvement effects in treating ischemic stroke and pulmonary embolism models, enhancing therapeutic efficiency and reducing side effects, providing new possibilities for personalized precision drug delivery.
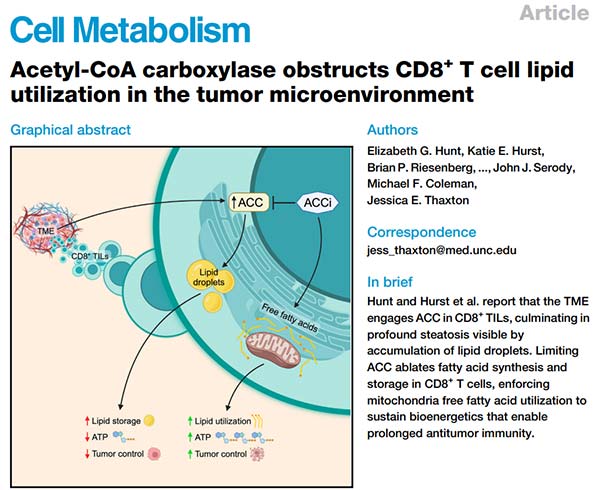
02 Acetyl-CoA carboxylase obstructs CD8+ T cell lipid utilization in the tumor microenvironment
Impact Factor: 29
Journal Name: Cell metabolism
CUSABIO Citation Product:
CSB-E12896m: Mouse malonyl coenzyme A ELISA kit
Research Highlights:
This study primarily investigates the impact of the tumor microenvironment (TME) on the lipid metabolism of CD8+ T cells. It is found that the TME, by activating the ACC enzyme, leads to the accumulation of lipid droplets and increased lipogenesis in CD8+ T cells, thereby inhibiting the fatty acid oxidation (FAO) pathway. Limiting ACC activity can restructure T cell metabolism, promote the utilization of FAO and ATP synthesis, thereby enhancing anti-tumor immunity. Additionally, ACC inhibitors also promote the persistence of CD8+ tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) and tumor control. These results reveal the key role of ACC in regulating T cell lipid metabolism, providing a new target for improving immunotherapy.
03 IgG is an aging factor that drives adipose tissue fibrosis and metabolic decline
Impact Factor: 29
Journal Name: Cell metabolism
CUSABIO Citation Product:
CSB-NP001601m: Mouse Immunoglobulin G
Research Highlights:
This paper reveals that immunoglobulin G (IgG) accumulates during aging and drives fibrosis and metabolic decline in adipose tissue, serving as a hidden factor leading to metabolic issues such as obesity and diabetes. It is discovered that IgG, by activating the Ras signaling pathway in macrophages, induces the TGF-尾/SMAD pathway, promoting fibrosis. Inhibiting the accumulation of IgG, such as by targeting its FcRn receptor in circulation, can extend healthy lifespan and improve metabolic health. This discovery provides a new perspective for understanding the metabolic mechanisms of aging and developing novel anti-aging strategies.
04 Bacteroides fragilis ubiquitin homologue drives intraspecies bacterial competition in the gut microbiome
Impact Factor: 28.3
Journal Name: Nature microbiology
CUSABIO Citation Product:
CSB-PA633459HA01EGW: dnaK Antibody
Research Highlights:
This study examines the intraspecies competitive mechanisms of Bacteroides fragilis, discovering that a ubiquitin homolog called BfUbb, secreted by the bacterium, exerts toxic effects on specific strains by non-covalently binding and inhibiting key peptidyl-prolyl isomerases (PPIases). The unique disulfide bond at the C-terminus of BfUbb is crucial for its antibacterial activity, achieved by binding to the tyrosine 119 residue on PPIases, enabling selective toxicity. The research reveals the competitive edge of BfUbb within the gut microbiota and its potential impact on the composition of the microbiome.
06 Recurrent infections drive persistent bladder dysfunction and pain via sensory nerve sprouting and mast cell activity
Impact Factor: 24.8
Journal Name: Science immunology
CUSABIO Citation Product:
CSB-E08357h: Human Substance P,SP ELISA Kit
Research Highlights:
This research uncovers the mechanisms behind chronic bladder dysfunction and pain caused by recurrent urinary tract infections (rUTI). Observations from patients and experimental mouse models reveal an increase in neuropeptides and sensory nerve sprouting in the bladders of rUTI patients, which is associated with nerve growth factor (NGF) produced by recruited monocytes and resident mast cells. The NGF-driven sensory sprouting and the continuous activation of mast cells are key mechanisms leading to pain and micturition abnormalities in rUTI patients, independent of bacterial presence.
07 Upregulation of CoQ shifts ferroptosis dependence from GPX4 to FSP1 in acquired radioresistance
Impact Factor: 24.3
Journal Name: Drug resistance updates
CUSABIO Citation Product:
CSB-E14081h: Human Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) ELISA Kit
Research Highlights:
This study finds that during the development of radioresistance in non-small cell lung cancer, there is a shift in cellular dependence on lipid peroxidation from glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4) to frataxin (FSP1). Overactivation of FSP1 reduces the sensitivity of cells to radiotherapy by increasing the synthesis of Coenzyme Q (CoQ) and decreasing the synthesis of glutathione (GSH). Inhibiting the FSP1-CoQ pathway may be a strategy to reverse radioresistance, and cholesterol synthesis inhibitors like simvastatin have shown potential to enhance the effectiveness of radiotherapy by blocking CoQ synthesis.
08 Cell surface patching via CXCR4-targeted nanothreads for cancer metastasis inhibition
Impact Factor: 16.6
Journal Name: Nature communications
CUSABIO Citation Product:
CSB-EL013041MO: Mouse Lysyl oxidase homolog 2(LOXL2) ELISA kit
Research Highlights:
This article mainly introduces a strategy to promote receptor aggregation and synchronize subsequent mechanotransduction by suturing a "patch" on the cell surface using nanowires. The strategy utilizes two types of interactive nanowires; first, nanowire 1 connects adjacent receptors and presents decoy receptors, then nanowire 2 targets these decoy receptors for multivalent binding, forming a helical supermolecular network with nanowire 1. This stepwise activation leads to the aggregation of a wide range of receptors, integrating mechanotransduction to interfere with signal transduction. When applied to inhibit CXCR4 expressed in metastatic breast cancer in mice, this approach induces and consolidates multiple events, including intercepting the metastasis cascade, reversing immunosuppression, and enhancing the effects of photodynamic immunotherapy, thereby reducing the metastatic burden. Overall, this work provides a versatile tool for spatially arranging cell surface receptors to improve therapeutic outcomes.
09 Cochaperones convey the energy of ATP hydrolysis for directional action of Hsp90
Impact Factor: 16.6
Journal Name: Nature communications
CUSABIO Citation Product:
CSB-EP326074SVG: Recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae Serine/threonine-protein kinase STE11 (STE11), partial
Research Highlights:
This study examines the energy utilization mechanism of the molecular chaperone Hsp90 when cooperating with other proteins (clients) within yeast cells. Through single-molecule FRET experiments, it is discovered that the directed movement of Hsp90 is associated with the binding of three essential cochaperones (Aha1, Sba1, and Cdc37), which introduce the energy from ATP hydrolysis into the conformational changes of Hsp90, enabling functional cyclic operations. The research reveals that the dynamic behavior of Hsp90 is not strictly dependent on ATP hydrolysis but is regulated through an upstream equilibrium state and subsequent directional steps.
10 Cbp1 and Cren7 form chromatin-like structures that ensure efficient transcription of long CRISPR arrays
Impact Factor: 16.6
Journal Name: Nature communications
CUSABIO Citation Product:
CSB-PA502491LA01FPB: creN7 Antibody
Research Highlights:
This paper investigates the functions of Cbp1 and Cren7 in the CRISPR array of archaea, finding that these two proteins regulate the transcription of the CRISPR array by forming a chromatin-like structure. Cbp1 not only directly recruits Cren7 but also suppresses the transcription of internal non-coding promoters while enhancing transcription driven by the CRISPR leader promoter. These findings reveal the key role of the Cbp1-Cren7 complex in regulating the expression of long CRISPR arrays, which is significant for understanding the archaeal immune system and transcriptional regulatory mechanisms.
23000+ Published Papers!
CUSABIO team. CUSABIO April Citations Review: 300 High-Impact Citations, Cumulative Impact Factor Exceeds 1500+!. https://www.cusabio.com/c-21174.html