Full Product Name
Rabbit anti-Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (Baker's yeast) RAD51 Polyclonal antibody
Alternative Names
RAD51 antibody; YER095W antibody; DNA repair protein RAD51 antibody
Species Reactivity
Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (Baker's yeast)
Immunogen
Recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (Baker's yeast) RAD51 protein
Immunogen Species
Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (Baker's yeast)
Purification Method
Protein A/G
Concentration
It differs from different batches. Please contact us to confirm it.
Buffer
Preservative: 0.03% Proclin 300
Constituents: 50% Glycerol, 0.01M PBS, pH 7.4
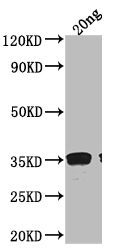
Tested Applications
ELISA, WB
Storage
Upon receipt, store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze.
Lead Time
Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time maybe differs from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.
Description
The recombinant Escherichia coli RAD51 protein is administered to a rabbit to trigger an immune response. Antibodies against the RAD51 protein are produced by the rabbit's immune system over time. After an adequate antibody response is generated, a serum sample is collected to obtain polyclonal antibodies. The RAD51 antibody undergoes protein A/G affinity chromatography purification. The effectiveness of the RAD51 antibody is assessed through ELISA and WB applications. This particular RAD51 antibody exhibits specific reactivity with the Escherichia coli RAD51 protein.
The RAD51 protein in Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) is a key player in homologous recombination. It mainly facilitates the exchange of genetic material between homologous DNA strands during the repair of double-strand breaks and the restart of stalled or collapsed replication forks. It is crucial for maintaining genome integrity and preventing the accumulation of mutations
Usage
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.