- A micro ELISA plate --- The 96-well plate has been pre-coated with an anti-human ECP antibody. This dismountable microplate can be divided into 12 x 8 strip plates.
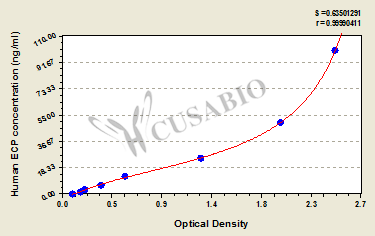
- Two vials lyophilized standard --- Dilute a bottle of the standard at dilution series, read the OD values, and then draw a standard curve.
- One vial Biotin-labeled ECP antibody (100 x concentrate) (120 μl/bottle) ---Act as the detection antibody.
- One vial HRP-avidin (100 x concentrate) (120 μl/bottle) --- Bind to the detection antibody and react with the TMB substrate to make the solution chromogenic.
- One vial Biotin-antibody Diluent (15 ml/bottle) ---Dilute the high concentration Biotin-antibody to an appropriate working solution.
- One vial HRP-avidin Diluent (15 ml/bottle) ---Dilute the high concentration HRP-avidin solution to an appropriate solution.
- One vial Sample Diluent (50 ml/bottle)---Dilute the sample to an appropriate concentration.
- One vial Wash Buffer (25 x concentrate) (20 ml/bottle) --- Wash away unbound or free substances.
- One vial TMB Substrate (10 ml/bottle) --- Act as the chromogenic agent. TMB interacts with HRP, eliciting the solution turns blue.
- One vial Stop Solution (10 ml/bottle) --- Stop the color reaction. The solution color immediately turns from blue to yellow.
- Four Adhesive Strips (For 96 wells) --- Cover the microplate when incubation.
- An instruction manual
- Home
- Products
Kits
- ELISA Kits
- Exosome Isolation Kits
- ELISA Kits For Food Safety & Drug Residues
- Plasmid DNA Purification Maxiprep Kit
- HCP Detection ELISA Kit
Antibodies- Recombinant Antibodies
- Monoclonal Antibodies
- Polyclonal Antibodies
- Secondary Antibodies
- Tag/Control Antibodies
- Small Molecular Antibodies
- ChIP Antibodies
- Antibody Pairs
- Custom Antibodies
- Modified Histone Antibodies
- Biosimilar Antibodies
Hot Categories- Mini Sample ELISA kit
- Inflammatory Factor ELISA Detection Panel
- Rare Species Antibodies
- Anti-CAR Linker Antibody
- Monkeypox Virus Research Related Products
- Anti-payload Antibodies
- Immunohistochemistry (IHC) Antibodies
- Flow Cytometry Antibodies
- IS Series Cytokine Detection ELISA Kit
- Recombinant DT3C protein
- Chemokine Receptors
- G protein-Coupled Receptor
- Recombinant Antibodies for Drug Discovery
- Recombinant Proteins for ADCs
- New Products Launch
- CRO Service
Quote for CRO Service Specialized CRO Services Protein Expression Services
- Transmembrane Protein Expression Service*
- E.coli Expression System
- Yeast Expression System
- In vitro E.coli Expression System
- Insect Baculovirus Expression System
- Mammalian Cell Expression System
- Pathways
- Technical Resources
- About Us
- Contact