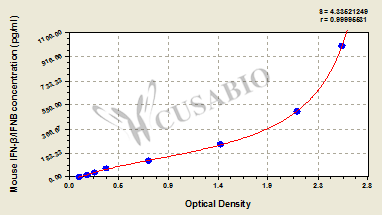
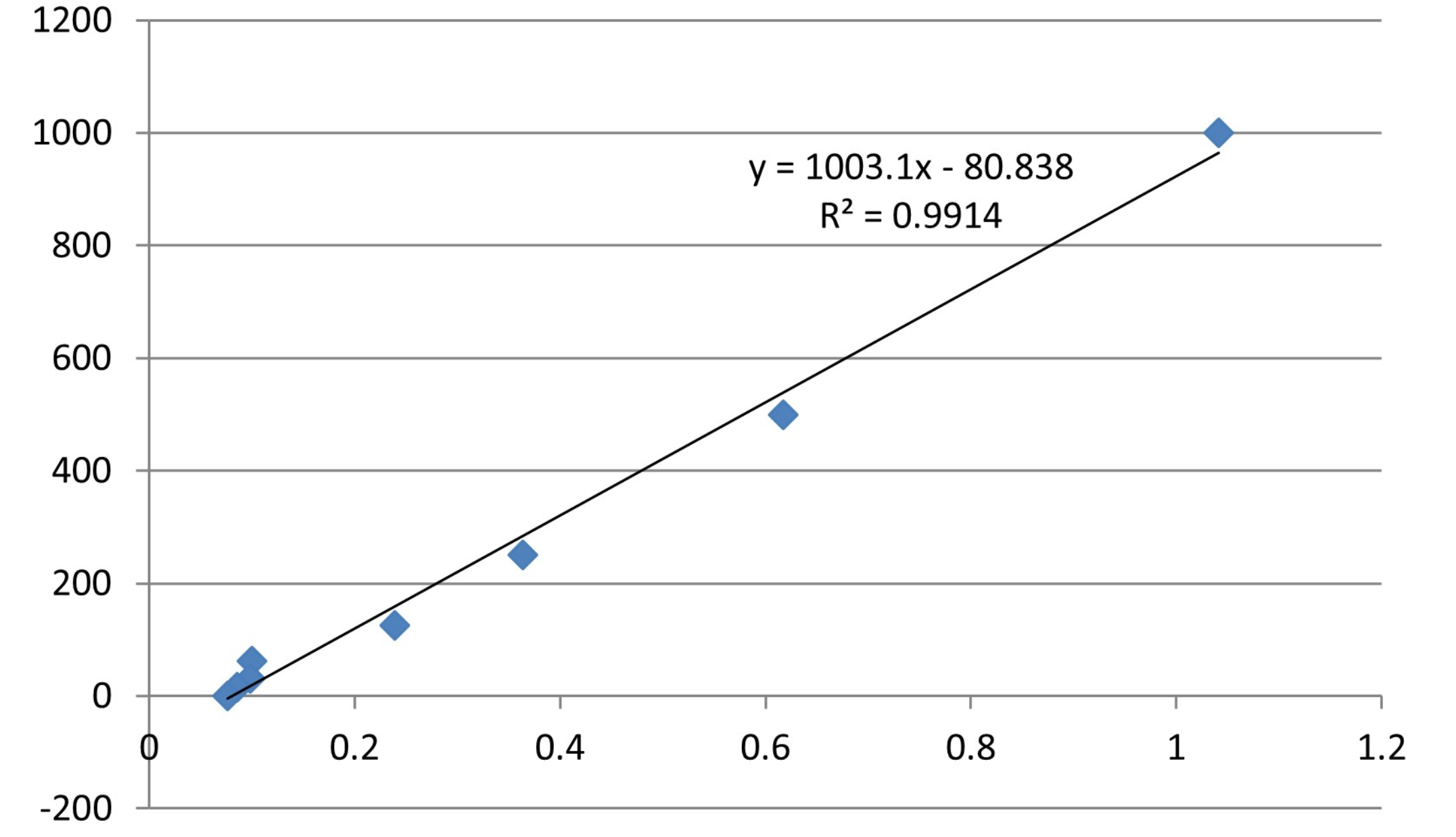
The mouse IFNB (IFNB) ELISA Kit quantitates mouse IFNB levels in multiple samples, including serum, plasma, cell culture supernates, tissue homogenates, and cell lysates. IFNB is an essential cytokine in promoting and regulating innate and adaptive immune responses. It has both anti-inflammatory and pro-inflammatory properties. IFNB binds to IFNAR1 and IFNAR2 and then activates JAK/STAT pathway, leading to the phosphorylation of STAT1 and STAT2 and the formation of the STAT1/STAT2/IRF3 complex, finally stimulating the expression of genes that encodes proteins exerting antiviral, antiproliferative, and antitumor effects. IFNB has been applied to multiple sclerosis treatment via the downregulation of the MHC class II expression in antigen-presenting cells, the induction of IL-10 synthesis, and the suppression of T cell migration. The antiviral and immunoregulatory effects of IFNB could be most effective if used in the early stages of COVID-19.
This kit employs the sandwich-ELISA mechanism in conjugation with IFNB antibody-IFNB antigen-specific binding as well as HRP-TMB chromogenic reaction to measure the concentration of IFNB in the samples. The kit is characterized by high sensitivity, strong specificity, good linearity, high recovery, and a precision of less than 10%.