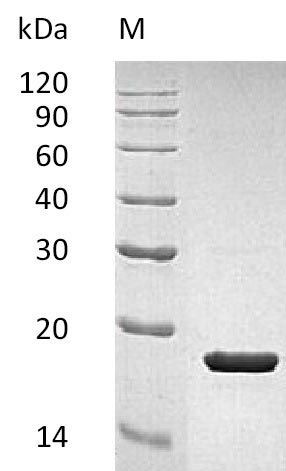
Recombinant Human Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist protein (IL1RN) gets produced in E. coli and contains the complete mature protein spanning amino acids 26 to 177. This tag-free protein achieves purity levels exceeding 95% when measured by SDS-PAGE, which appears to ensure solid quality for research applications. The biological activity of IL1RN has been confirmed, showing an ED50 of 13.2 ng/mL based on its capacity to block IL-1 beta induced NF-kB signaling in 293-IL1 Res cells. Endotoxin levels stay below 1.0 EU/µg, as measured through the LAL method.
Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist (IL1RN) serves as a key protein that works to block interleukin-1 activities by attaching to its receptor, effectively stopping signal transmission. It likely plays a major role in controlling immune and inflammatory responses, which makes it particularly important for research into immune regulation and inflammatory diseases. Studying how IL1RN interacts with its receptor may help clarify the pathways involved in inflammation and immune response control.
Potential Applications
Note: The applications listed below are based on what we know about this protein's biological functions, published research, and experience from experts in the field. However, we haven't fully tested all of these applications ourselves yet. We'd recommend running some preliminary tests first to make sure they work for your specific research goals.
1. IL-1β Signaling Pathway Inhibition Studies
This recombinant IL1RN is confirmed to be biologically active (ED₅₀ 13.2 ng/mL in NF-κB inhibition) and suitable for IL-1β signaling inhibition studies. However, the E. coli expression produces a non-glycosylated protein, which may affect stability or half-life compared to native glycosylated IL1RN. Researchers should validate that inhibition kinetics and duration match mammalian-expressed IL1RN, particularly in long-term assays. The competitive antagonism mechanism is well-supported by the demonstrated activity.
2. Anti-IL1RN Antibody Development and Validation
This high-purity, tag-free IL1RN serves as an excellent antigen for antibody development. However, antibodies generated against this E. coli-expressed protein may not recognize glycosylated epitopes present in native IL1RN from human sources. Comprehensive validation should include testing against mammalian-expressed or naturally occurring IL1RN to ensure recognition of physiological forms. The confirmed bioactivity supports the development of function-blocking antibodies.
3. Inflammatory Response Modulation in Cell Culture Models
The protein is appropriate for inflammation studies, but the ED₅₀ was determined in 293-IL1 Res cells, which may not fully represent primary immune cells or complex inflammatory environments. Researchers should validate optimal concentrations in primary macrophages, fibroblasts, or other relevant cell types. The low endotoxin ensures specific attribution of effects to IL1RN activity rather than contamination.
4. Protein-Protein Interaction Studies
The biologically active IL1RN is suitable for interaction studies with IL-1 receptors, but the non-glycosylated state may alter binding kinetics compared to native IL1RN. While the tag-free design ensures authentic interactions, binding affinity should be validated against mammalian-expressed IL1RN for precise measurements. The mature protein sequence contains all necessary domains for receptor binding.
5. Cytokine Network Analysis in Co-culture Systems
The protein can be used in co-culture systems, but the E. coli expression and lack of glycosylation may affect diffusion and stability in complex 3D environments. Researchers should validate that IL-1β inhibition efficacy matches mammalian-expressed IL1RN, particularly in long-term co-cultures where protein stability becomes critical. The specific activity provides a good starting point for dose optimization.
Final Recommendation & Action Plan
This E. coli-expressed human IL1RN is a high-quality functional reagent with confirmed bioactivity, making it suitable for most proposed applications. However, researchers should account for its non-glycosylated state and validate key findings in physiologically relevant systems. For immediate use: employ it at 10-50 ng/mL based on the ED₅₀, but establish dose-response curves in each specific cell type and assay format. When developing antibodies, this protein is ideal for generating reagents, but validated against native IL1RN from inflammatory conditions to ensure recognition of physiological forms. For signaling studies, the tag-free design ensures authentic receptor interactions, but confirms inhibition kinetics in primary cells. In co-culture systems, monitor protein stability and replenish as needed for long-term experiments. The low endotoxin is particularly valuable for sensitive primary cell assays. Always include appropriate controls and consider that different cell types may exhibit varying sensitivity to IL1RN-mediated inhibition based on IL-1 receptor expression levels.