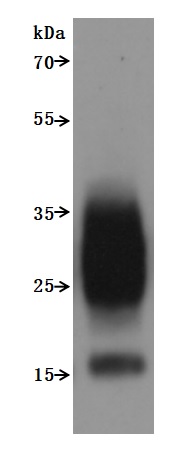
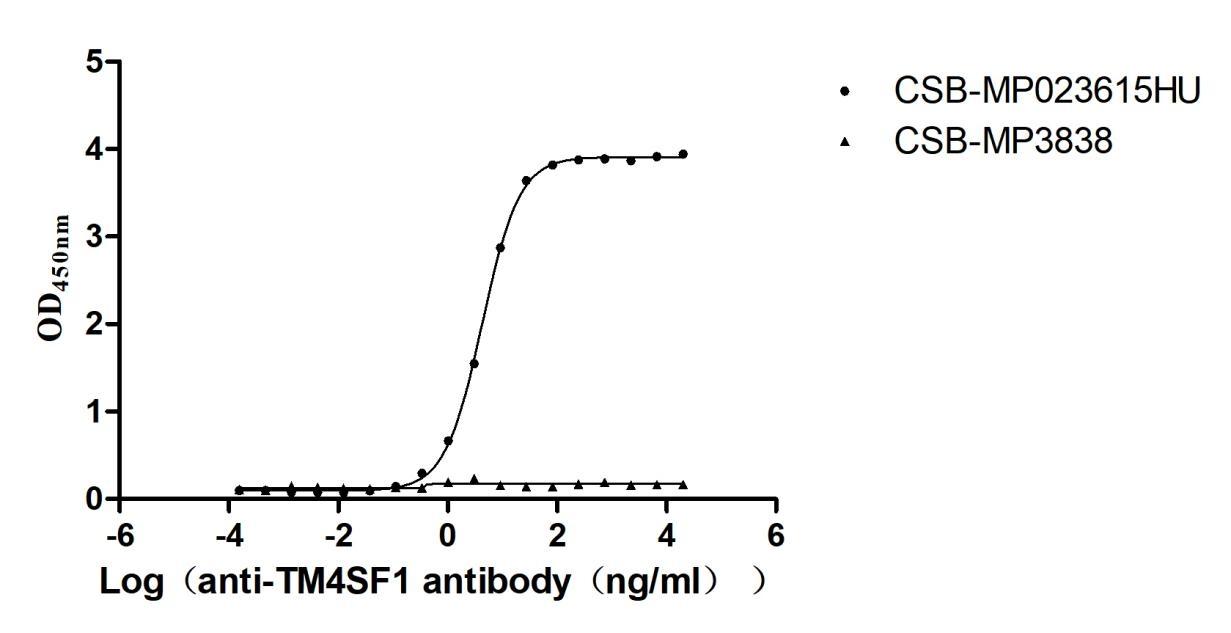
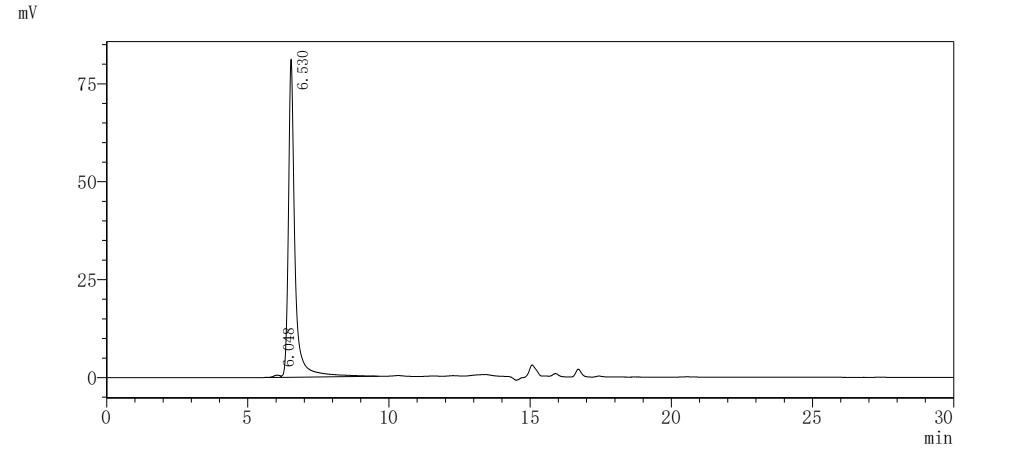
The full-length human TM4SF1 (residues 1-202) is expressed as a virus-like particle (VLP) in mammalian cells with a C-terminal 10×His tag, maintaining native transmembrane topology and multi-pass membrane protein conformation. The recombinant TM4SF1 protein exhibits exceptional purity (>95% by SEC-HPLC) and low endotoxin content (<1.0 EU/μg, LAL method). Its bioactivity has been validated through functional ELISA demonstrating specific antibody binding (EC50: 4.079–4.472 ng/mL at 5 μg/mL immobilization), with VLPs (CSB-MP3838) as negative controls. Mammalian expression ensures proper post-translational modifications critical for TM4SF1's role in cell adhesion, metastasis, and tumor microenvironment regulation. The VLP structure preserves quaternary interactions, enhancing antigen presentation for antibody validation. Lyophilized for stability, this protein facilitates studies of TM4SF1-mediated oncogenic signaling, therapeutic target discovery, and diagnostic assay development in cancer research.
The human TM4SF1 protein, a member of the tetraspanin superfamily, is significantly implicated in various critical cellular processes, particularly in the context of cancer biology. This protein aids in organizing lipid microdomains in the plasma membrane, facilitating interactions with other membrane proteins, including integrins, which are crucial for cell adhesion, migration, and cell signaling [1][2]. TM4SF1 is overexpressed in numerous malignancies, including breast, pancreatic, and lung cancers, suggesting its role as a significant player in cancer progression and metastasis [2][3][4].
Research indicates that TM4SF1 significantly influences tumor behavior through its capacity to modulate cell motility and invasion. For instance, it has been shown to enhance the invasive properties of cancer cells by promoting the formation of nanopodia—cellular protrusions vital for dynamic cellular interactions with their environment [1][5]. Additionally, TM4SF1 is involved in key signaling pathways that govern processes such as cell proliferation and survival, acting as both an oncogene and a potential target for therapeutic intervention [3][6].
TM4SF1's expression is also linked to cellular activities within the tumor microenvironment. In endothelial cells, TM4SF1 regulates functions essential for angiogenesis, such as filopodia formation and cellular migration, which are critical for sustaining tumor growth and metastasis [5][7][8]. Moreover, it is associated with multiple signaling cascades, including those modulated by AKT, which may further enhance the malignant characteristics of tumors [7][4]. The regulation of TM4SF1 by various microRNAs, such as miR-206 and hsa-miR-141, suggests that TM4SF1's activity can be finely tuned post-transcriptionally, adding another layer of complexity to its role in tumor biology [9].
Furthermore, studies have indicated that TM4SF1 is not only a marker of malignancy but may also act as a prognostic factor. Its elevated expression correlates with poor clinical outcomes in various cancers, as seen in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma [10]. The ongoing research on TM4SF1 indicates potential applications in targeted cancer therapies, focusing on its ability to mediate drug resistance and its potential as a biomarker for tumor progression and metastasis [6][11].
References:
[1] L. Xu, Q. Li, et al. Hsa-mir-141 downregulates tm4sf1 to inhibit pancreatic cancer cell invasion and migration. International Journal of Oncology, vol. 44, no. 2, p. 459-466, 2013. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.2013.2189
[2] Z. Luan, J. Zhang, & Y. Wang. Identification of marker genes for spinal cord injury. Frontiers in Medicine, vol. 11, 2024. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2024.1364380
[3] P. Wang, W. Bao, G. Zhang, H. Cui, & G. Shi. Transmembrane-4-l-six-family-1, a potential predictor for poor prognosis, overexpressed in human glioma. Neuroreport, vol. 26, no. 8, p. 455-461, 2015. https://doi.org/10.1097/wnr.0000000000000370
[4] C. Gao, H. Yao, H. Liu, Y. Feng, & Z. Yang. Tm4sf1 is a potential target for anti-invasion and metastasis in ovarian cancer. BMC Cancer, vol. 19, no. 1, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-019-5417-7
[5] A. Zukauskas, A. Merley, et al. Tm4sf1: a tetraspanin-like protein necessary for nanopodia formation and endothelial cell migration. Angiogenesis, vol. 14, no. 3, p. 345-354, 2011. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-011-9218-0
[6] J. Cao, J. Yang, et al. Tm4sf1 promotes gemcitabine resistance of pancreatic cancer in vitro and in vivo. Plos One, vol. 10, no. 12, p. e0144969, 2015. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0144969
[7] R. Wang, L. Sun, et al. B7-h3 suppresses doxorubicin-induced senescence-like growth arrest in colorectal cancer through the akt/tm4sf1/sirt1 pathway. Cell Death and Disease, vol. 12, no. 5, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-021-03736-2
[8] C. Lin, A. Merley, H. Wada, J. Zheng, & S. Jaminet. Tm4sf1 is essential for embryonic blood vessel development. 2023. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-3245895/v1
[9] Y. Park, S. Seo, et al. Mirna-206 suppresses pge2-induced colorectal cancer cell proliferation, migration, and invasion by targetting tm4sf1. Bioscience Reports, vol. 38, no. 5, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1042/bsr20180664
[10] B. Zheng, K. Ohuchida, et al. Tm4sf1 as a prognostic marker of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma is involved in migration and invasion of cancer cells. International Journal of Oncology, vol. 47, no. 2, p. 490-498, 2015. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.2015.3022
[11] J. Cao, J. Yang, et al. Tm4sf1 regulates pancreatic cancer migration and invasion in vitro and in vivo. Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry, vol. 39, no. 2, p. 740-750, 2016. https://doi.org/10.1159/000445664