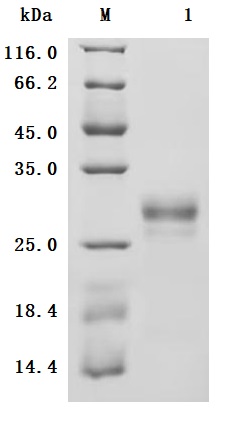
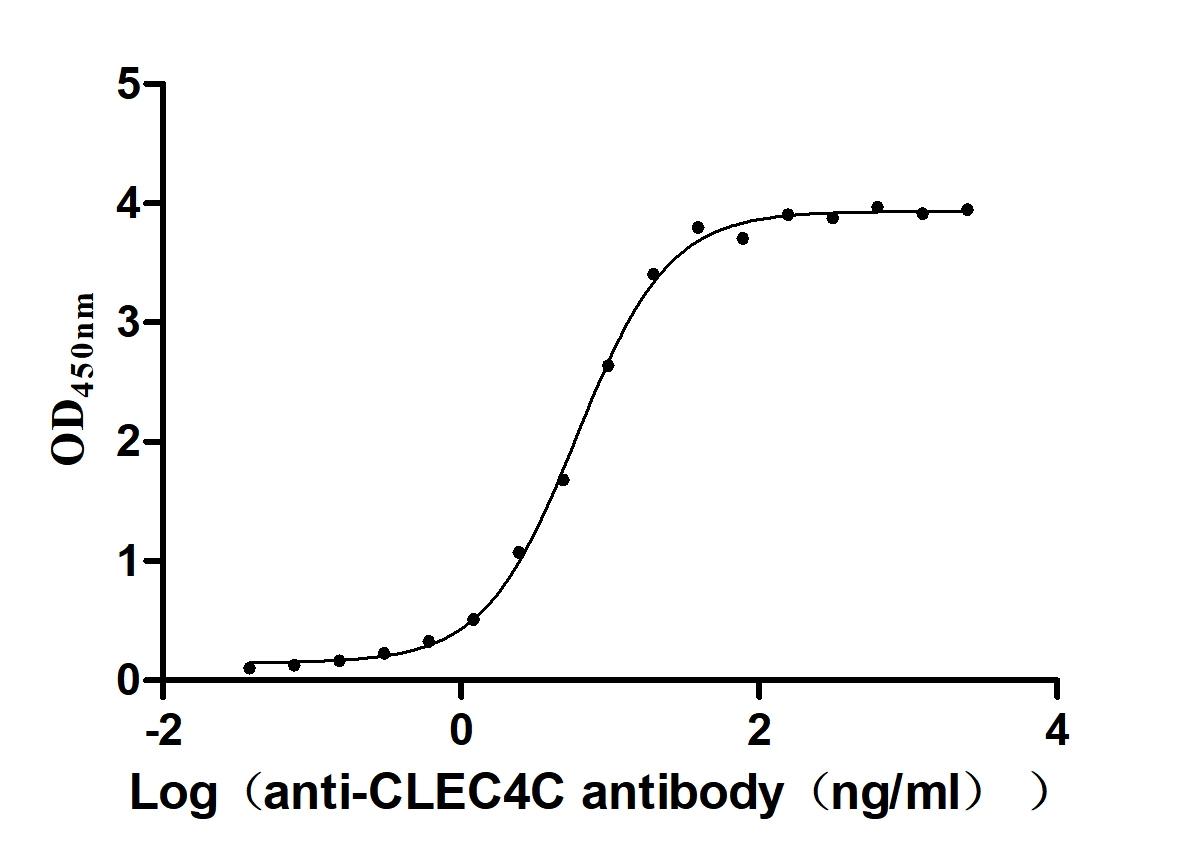
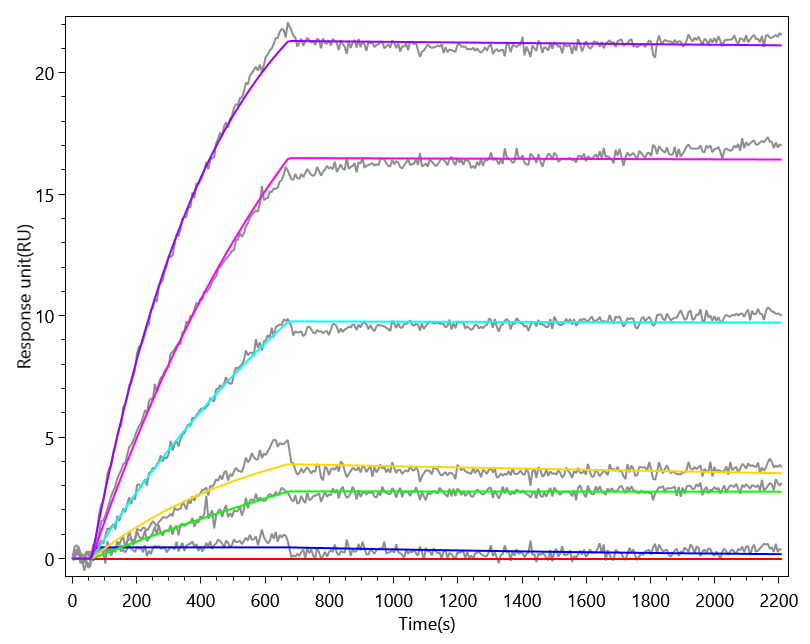
This biologically active recombinant Macaca fascicularis CLEC4C is expressed in mammalian cells, encompassing residues 48-212 of CLEC4C, with an N-terminal 6×His-Myc tag. The recombinant CLEC4C protein exhibits high purity (>95% by SDS-PAGE) and low endotoxin levels (<1.0 EU/μg, LAL method), ensuring suitability for immunological studies. Functional analysis via ELISA confirms specific binding to anti-CLEC4C antibody(CSB-RA855470MA1HU) with an EC50 of 5.506–6.472 ng/mL when immobilized at 2 μg/mL, validating its structural integrity and antigenic properties. Mammalian expression ensures proper glycosylation and folding, which are critical for CLEC4C’s role in pathogen recognition and dendritic cell signaling. Presented as lyophilized powder, this preparation combines stability with ease of reconstitution. The dual 6×His-Myc tag facilitates purification and detection while preserving functional epitopes. This recombinant CLEC4C protein serves as a key tool for studying lectin-mediated immune responses, viral entry mechanisms, and therapeutic antibody development targeting CLEC4C-associated pathways in infectious diseases and immunology research.
The CLEC4C protein, which is a C-type lectin, plays a significant role in the immune response of cynomolgus macaques (Macaca fascicularis), a species commonly used as a non-human primate model in biomedical research. CLEC4C is involved in the recognition of specific carbohydrates on pathogens, contributing to the immune response against infections, although specific citations reflecting this function in cynomolgus macaques were not retrievable [1][2].
Cynomolgus macaques have been instrumental in understanding immune mechanisms through the study of proteins such as CLEC4C, particularly in contexts related to viral challenges such as SARS-CoV-2. Research has shown that different immune gene expressions can significantly vary between macaque species, which is crucial for evaluating vaccine efficacy and immune responses during experimental infections [2] and supports the idea that these animals are relevant for understanding the immune response dynamics [3]. Furthermore, their anatomical and physiological similarities to humans enhance their translational relevance in immunological studies [4].
Studies utilizing cynomolgus macaques have indicated that immunological pathways involving C-type lectins, like CLEC4C, are significant for recognizing pathogens and shaping adaptive immune responses in a model that closely resembles human conditions. These proteins' expression levels and functional properties may provide insights into the susceptibility of these animals to various infectious diseases, including those caused by zoonotic pathogens [4]. Therefore, understanding CLEC4C in Macaca fascicularis is vital for leveraging this species in vaccine development and infectious disease research.
References:
[1] A. Higashino, R. Sakate, et al. Whole-genome sequencing and analysis of the malaysian cynomolgus macaque (macaca fascicularis) genome. Genome Biology, vol. 13, no. 7, 2012. https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2012-13-7-r58
[2] F. Salguero, A. White, et al. Comparison of rhesus and cynomolgus macaques as an infection model for covid-19. Nature Communications, vol. 12, no. 1, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-21389-9
[3] E. Hobbs and T. REID. Animals and sars‐cov‐2: species susceptibility and viral transmission in experimental and natural conditions, and the potential implications for community transmission. Transboundary and Emerging Diseases, vol. 68, no. 4, p. 1850-1867, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1111/tbed.13885
[4] G. Doxiadis, A. Vos-Rouweler, N. Groot, Ń. Otting, & R. Bontrop. Dr haplotype diversity of the cynomolgus macaque as defined by its transcriptome. Immunogenetics, vol. 64, no. 1, p. 31-37, 2011. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00251-011-0561-5