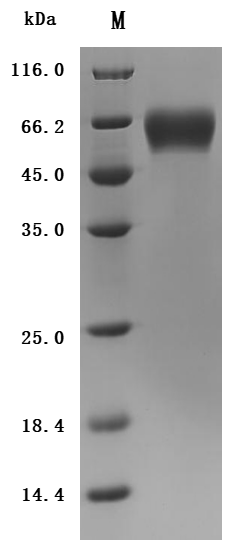
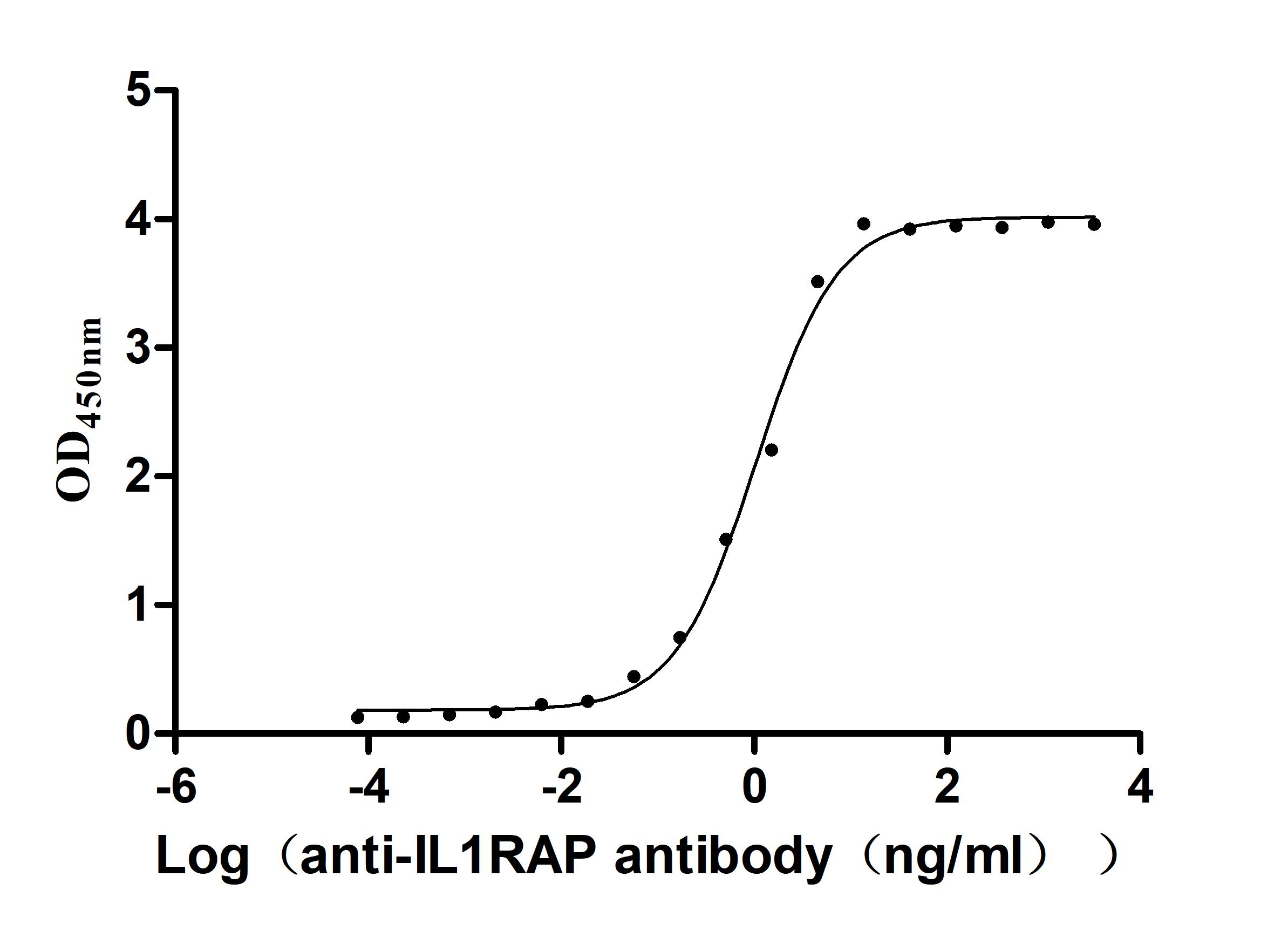
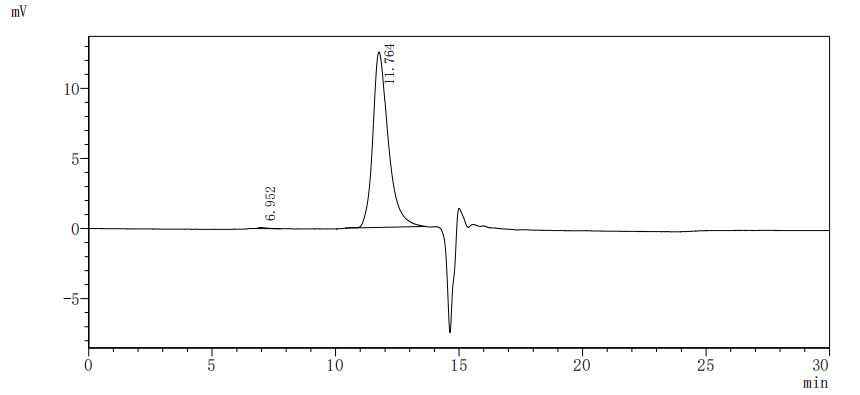
The recombinant Macaca fascicularis IL1RAP protein is a functionally active construct produced in mammalian cells, ensuring accurate protein folding and post-translational modifications. It includes amino acids 21 to 359 of the native IL1RAP sequence and is fused with a C-terminal 10xHis tag to facilitate purification and downstream applications. Supplied as a lyophilized powder, the recombinant IL1RAP protein meets high purity standards, exceeding 95% as determined by both SDS-PAGE and SEC-HPLC. Endotoxin levels are maintained below 1.0 EU/µg, confirmed by LAL testing, making it suitable for use in sensitive biological assays. Functional validation was performed via ELISA, where the immobilized protein at 2 μg/mL binds specifically to the anti-IL1RAP recombinant antibody (CSB-RA878844MA1HU), with an EC50 ranging from 0.9099 to 1.181 ng/mL. This confirms its strong bioactivity and utility in immunological or receptor-binding research contexts.
The IL1RAP is a crucial component in the signaling pathways mediated by the IL-1 family of cytokines. In Macaca fascicularis, as well as other mammals, IL1RAP is essential for the formation of functional IL-1 receptor complexes that initiate pro-inflammatory signaling cascades critical for various physiological and pathological processes.
IL-1, particularly IL-1β, exerts its effects by binding to IL-1R1, which subsequently recruits IL1RAP to form a heterodimeric receptor complex. This assembly activates intracellular signaling pathways, including those involving NF-κB and MAPK (Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase) pathways, necessary for the expression of inflammatory molecules and the modulation of immune responses [1][2]. Research indicates that IL1RAP is indispensable for the effective transduction of IL-1 signaling, as it aids in receptor dimerization and the recruitment of downstream signaling proteins like MyD88 and IL-1 receptor-associated kinases [1][3].
Moreover, studies have highlighted IL1RAP's role in macrophage activation and inflammation, where it influences cytokine production in response to infections. For instance, IL1RAP is involved in the inflammatory response to pathogens such as Burkholderia mallei, as observed in profiling studies using serum from infected Macaca fascicularis [4]. Furthermore, there is evidence suggesting that manipulation of IL1RAP expression can significantly alter immune responses, indicating its potential as a therapeutic target for inflammatory diseases [5][6].
In addition, its evolutionary conservation across different primate species points to its fundamental biological importance, particularly in the context of immune responses and disease models. The interaction between IL-1β and its receptor complex, including IL1RAP, has implications for various health conditions, including periodontal disease, where the upregulation of IL-1 signaling is associated with tissue inflammation and degradation [7][8].
References:
[1] J. Markovics, J. Araya, et al. Interleukin-1β induces increased transcriptional activation of the transforming growth factor-β-activating integrin subunit β8 through altering chromatin architecture. Journal of Biological Chemistry, vol. 286, no. 42, p. 36864-36874, 2011. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.m111.276790
[2] S. Lavalette, W. Raoul, et al. Interleukin-1β inhibition prevents choroidal neovascularization and does not exacerbate photoreceptor degeneration. American Journal of Pathology, vol. 178, no. 5, p. 2416-2423, 2011. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajpath.2011.01.013
[3] И. Кутырев, B. Cleveland, T. Leeds, & G. Wiens. Proinflammatory cytokine and cytokine receptor gene expression kinetics following challenge with flavobacterium psychrophilum in resistant and susceptible lines of rainbow trout (oncorhynchus mykiss). Fish & Shellfish Immunology, vol. 58, p. 542-553, 2016. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2016.09.053
[4] T. Glaros, C. Blancett, T. Bell, M. Natesan, & R. Ulrich. Serum biomarkers of burkholderia mallei infection elucidated by proteomic imaging of skin and lung abscesses. Clinical Proteomics, vol. 12, no. 1, 2015. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12014-015-9079-4
[5] M. Heuvel, L. Scholtens, E. Turk, D. Mantini, W. Vanduffel, & L. Barrett. Multimodal analysis of cortical chemoarchitecture and macroscale fmri resting‐state functional connectivity. Human Brain Mapping, vol. 37, no. 9, p. 3103-3113, 2016. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.23229
[6] S. Sugawara, R. Reeves, & S. Jost. Learning to be elite: lessons from hiv-1 controllers and animal models on trained innate immunity and virus suppression. Frontiers in Immunology, vol. 13, 2022. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2022.858383
[7] Y. Shimazaki, Y. Egami, et al. Relationship between obesity and physical fitness and periodontitis. Journal of Periodontology, vol. 81, no. 8, p. 1124-1131, 2010. https://doi.org/10.1902/jop.2010.100017
[8] N. Hengartner, J. Fiedler, A. Ignatius, & R. Brenner. Il-1β inhibits human osteoblast migration. Molecular Medicine, vol. 19, no. 1, p. 36-42, 2013. https://doi.org/10.2119/molmed.2012.00058