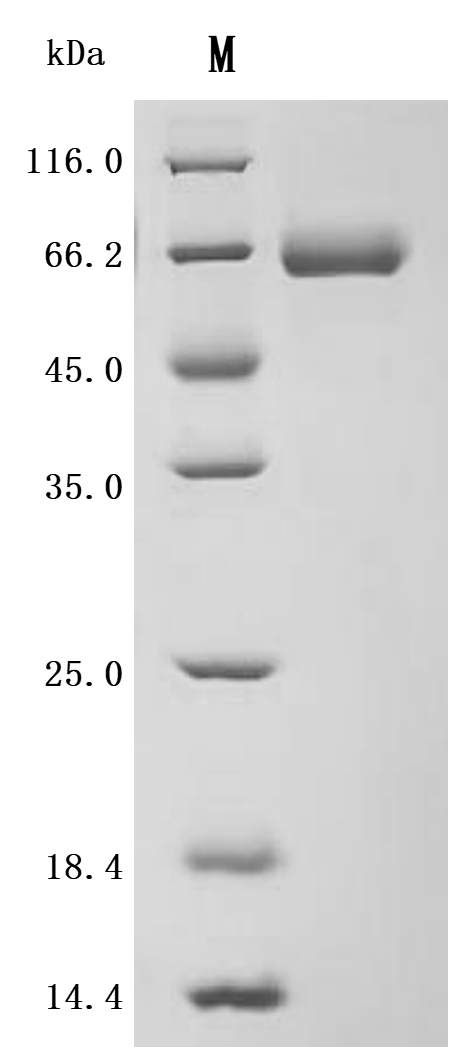
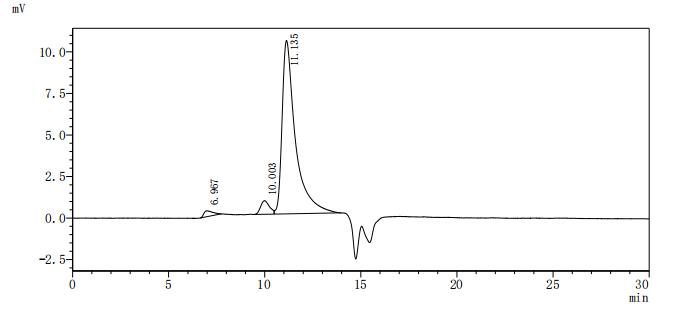
The recombinant mouse ALPG is an enzymatically active protein expressed in mammalian cells, comprising amino acids 19 to 502 of the native ALPG sequence. It is engineered with a C-terminal 10xHis tag to support purification and assay compatibility. The protein is supplied as a lyophilized powder and exhibits high purity, over 95% by SDS-PAGE and above 90% by SEC-HPLC. Endotoxin levels are tightly controlled, measuring less than 1.0 EU/μg by the LAL method. Functionally, the recombinant ALPG protein displays robust enzymatic activity, with a specific activity greater than 6000 U/mg. One unit corresponds to the amount of enzyme needed to cleave 1 nmol of p-nitrophenylphosphate (pNPP) per minute at 37°C and pH 10.0.
ALPG is one of the four major isoenzymes of alkaline phosphatase encoded in the human genome, alongside intestinal alkaline phosphatase (ALPI), tissue-nonspecific alkaline phosphatase (ALPL), and placental alkaline phosphatase (ALPP) [1][2][3]. Each of these isoenzymes exhibits specificity in terms of expression and physiological functions. ALPG is particularly vital in reproductive biology, as its expression is closely associated with germ cell development and function during spermatogenesis and early embryonic development.
Research indicates that ALPG plays a significant role in the differentiation of trophectoderm in early human embryos, which is critical for successful implantation and placentation [1]. This isoenzyme is noted for its expression during early stages of human development and its involvement in the first cellular differentiation within the inner cell mass, indicating its fundamental role in reproductive processes [1][4]. Furthermore, studies on genetically modified mouse models have implicated the expression of ALPG in regulating early germ cell development and differentiation, suggesting that alkaline phosphatases are essential for maintaining the integrity of germ cell lineage during critical stages of development [5][6].
The activity of ALPG may also reflect underlying cellular processes related to phosphomonoester hydrolysis, contributing to the availability of inorganic phosphate, which is crucial for various metabolic pathways within germ cells [3][7]. Abnormalities in ALPG expression or function have been linked to reproductive issues, including infertility, highlighting its role in normal spermatogenesis and germ line development [5][6]. Moreover, the expression of ALPG in contexts such as endometrial tissue emphasizes its potential role in reproductive health and associated pathologies [6].
References:
[1] Y. Yu, K. Rong, et al. The structural pathology for hypophosphatasia caused by malfunctional tissue non-specific alkaline phosphatase. Nature Communications, vol. 14, no. 1, 2023. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-39833-3
[2] R. Reetu, R. Gujjarappa, & C. Malakar. Recent advances in synthesis and medicinal evaluation of 1,2‐benzothiazine analogues. Asian Journal of Organic Chemistry, vol. 11, no. 8, 2022. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajoc.202200163
[3] B. Deracinois, S. Duban‐Deweer, G. Pottiez, R. Cecchelli, Y. Karamanos, & C. Flahaut. Tnap and ehd1 are over-expressed in bovine brain capillary endothelial cells after the re-induction of blood-brain barrier properties. Plos One, vol. 7, no. 10, p. e48428, 2012. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0048428
[4] Y. Shitara, R. Konno, et al. Host-derived protein profiles of human neonatal meconium across gestational ages. Nature Communications, vol. 15, no. 1, 2024. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-49805-w
[5] M. Tachibana, M. Nozaki, N. Takeda, & Y. Shinkai. Functional dynamics of h3k9 methylation during meiotic prophase progression. The Embo Journal, vol. 26, no. 14, p. 3346-3359, 2007. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.emboj.7601767
[6] M. Asaduzzaman, I. Pavlov, et al. Phosphorylation of zearalenone retains its toxicity. 2024. https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.07.30.605906
[7] D. Zaher, M. El‐Gamal, et al. Recent advances with alkaline phosphatase isoenzymes and their inhibitors. Archiv Der Pharmazie, vol. 353, no. 5, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1002/ardp.202000011