Function
Receptor for apelin receptor early endogenous ligand (APELA) and apelin (APLN) hormones coupled to G proteins that inhibit adenylate cyclase activity. Plays a key role in early development such as gastrulation, blood vessels formation and heart morphogenesis by acting as a receptor for APELA hormone. May promote angioblast migration toward the embryonic midline, i.e. the position of the future vessel formation, during vasculogenesis. Promotes sinus venosus (SV)-derived endothelial cells migration into the developing heart to promote coronary blood vessel development. Plays also a role in various processes in adults such as regulation of blood vessel formation, blood pressure, heart contractility and heart failure.; (Microbial infection) Alternative coreceptor with CD4 for HIV-1 infection; may be involved in the development of AIDS dementia.
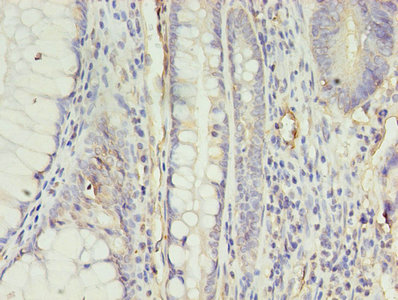
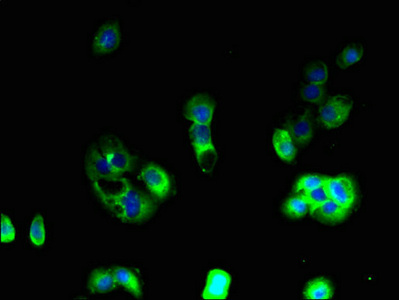
Tissue Specificity
Expressed in heart, brain, kidney, stomach, spleen, thymus, lung, ovary, small intestine and colon, adipose tissues and pancreas. Expressed in glial cells, astrocytes and neuronal subpopulations. Expressed in embryonic (ESCs) and induced (iPSCs) pluripote