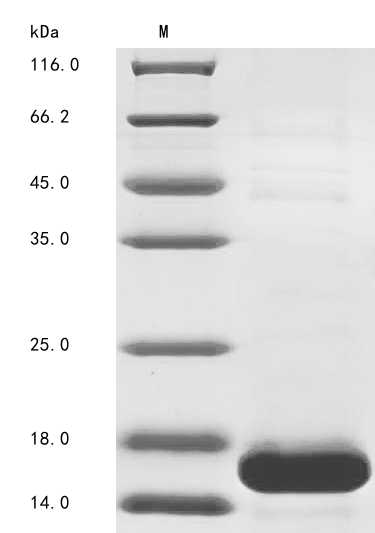
Recombinant Arabidopsis thaliana EPIDERMAL PATTERNING FACTOR-like protein 9 (EPFL9) is produced using an E. coli expression system and includes the mature protein region from amino acids 32 to 102. The product comes with an N-terminal 10xHis-tag, which streamlines purification and detection processes. SDS-PAGE analysis confirms the protein reaches greater than 85% purity, suggesting it provides reliable material for research applications.
EPFL9 belongs to the EPIDERMAL PATTERNING FACTOR-like family in Arabidopsis thaliana. This family appears to play a crucial role in regulating stomatal development and patterning in plants. The protein seems particularly relevant for research aimed at understanding epidermal cell differentiation mechanisms and intercellular signaling pathways in plant biology. Many researchers find this protein useful when studying plant growth and development.
Potential Applications
Note: The applications listed below are based on what we know about this protein's biological functions, published research, and experience from experts in the field. However, we haven't fully tested all of these applications ourselves yet. We'd recommend running some preliminary tests first to make sure they work for your specific research goals.
EPFL9 is a plant signaling peptide that typically requires proper disulfide bond formation and specific tertiary structure for its biological activity in epidermal patterning. E. coli expression systems often struggle with the correct folding of small eukaryotic signaling proteins that require specific post-translational modifications or oxidative folding environments. The relatively large 10xHis tag (compared to the small mature protein size of 70aa) may significantly interfere with the protein's native conformation and functional domains. No validation data (e.g., receptor binding assays, circular dichroism) are provided. Therefore, the protein's folding status and bioactivity cannot be confirmed and are likely compromised.
1. Protein-Protein Interaction Studies Using Pull-Down Assays
This application carries substantial risk without folding validation. If correctly folded, the His-tagged EPFL9 could theoretically be used to identify binding partners, but the large tag may sterically hinder proper interactions even with correct folding. More realistically, if misfolded (probable in E. coli), the protein will exhibit non-specific binding patterns that do not reflect biological interactions, leading to misleading conclusions about epidermal patterning mechanisms.
2. Antibody Development and Validation
This application remains feasible as antibody development relies on linear epitope recognition. The defined amino acid sequence and high purity support consistent immunization results. However, antibodies generated against potentially misfolded protein may not optimally recognize the native, properly folded EPFL9 in plant tissues, particularly for conformation-dependent epitopes important for biological function.
3. Biochemical Characterization and Structural Studies
This application requires proper folding validation. If correctly folded, the protein could be used for limited structural characterization. However, if misfolded, biophysical data would misrepresent the native protein's properties. The large His-tag relative to the small protein size may dominate the structural signals, making meaningful analysis of the native EPFL9 structure challenging.
4. Competitive Binding Assays with Related EPFL Family Members
This application is not recommended without folding and functional validation. Competitive binding studies require properly folded proteins with maintained structural integrity. The misfolded recombinant protein will not exhibit correct binding specificity or affinity, making comparative data with other EPFL proteins biologically irrelevant and potentially misleading for understanding functional relationships within this protein family.
Final Recommendation & Action Plan
This E. coli-expressed His-tagged EPFL9 is high-risk for functional studies due to the challenges of producing properly folded small signaling peptides in prokaryotic systems and the significant tag interference relative to the small protein size. Before any application, rigorous validation of protein folding must be performed using analytical methods such as circular dichroism spectroscopy to assess secondary structure, and functional validation through receptor binding assays if possible. For reliable results, consider alternative expression systems such as eukaryotic hosts (e.g., plant-based or insect cell systems) that better support proper disulfide bond formation and folding of plant signaling peptides. Antibody development can proceed with the understanding that resulting antibodies may require additional validation for native protein recognition in plant tissues. Competitive binding and interaction studies should be avoided unless proper folding and functionality are conclusively demonstrated.