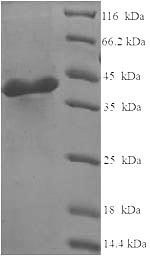
The gene encoding the Human C1QA protein (23-245aa) is incorporated into a plasmid vector to generate recombinant plasmid, which is then introduced into e.coli cells. The e.coli cells containing the recombinant plasmid are selected and cultured under conditions that stimulate the expression of the gene of interest. A N-terminal 6xHis-SUMO tag is attached to the protein. After expression, affinity purification is employed to isolate and purify the recombinant Human C1QA protein from the cell lysate. Denaturing SDS-PAGE is utilized to resolve the resulting recombinant Human C1QA protein, revealing a purity level exceeding 90%.