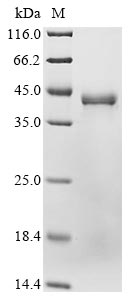
Recombinant Human Glutaminyl-peptide cyclotransferase (QPCT) is produced in a mammalian cell expression system, which appears to ensure proper folding and post-translational modifications. The protein includes the full length of the mature protein, covering amino acids 29-361, and features an N-terminal 10xHis-tag for simplified purification and detection. SDS-PAGE analysis confirms the protein purity exceeds 90%, which likely makes it suitable for various research applications.
Glutaminyl-peptide cyclotransferase (QPCT) is an enzyme that participates in post-translational modification processes. It catalyzes the formation of pyroglutamate from glutaminyl residues at the N-terminus of peptides and proteins. This modification may influence protein stability and function. QPCT holds significance in research related to protein maturation and degradation pathways, and its activity proves relevant in studies focusing on enzyme mechanics and protein biochemistry.
Potential Applications
Note: The applications listed below are based on what we know about this protein's biological functions, published research, and experience from experts in the field. However, we haven't fully tested all of these applications ourselves yet. We'd recommend running some preliminary tests first to make sure they work for your specific research goals.
The mammalian expression system is advantageous for producing a human enzyme, as it is more likely to support proper eukaryotic folding environments and any necessary post-translational modifications compared to prokaryotic systems like E. coli. This increases the probability that the protein could be correctly folded. While the mammalian expression system is favorable, the correct folding and bioactivity of this specific recombinant QPCT protein batch must be experimentally verified before it can be confidently used in functional studies. It cannot be assumed to be bioactive based on the production information alone.
1. Biochemical Characterization and Enzyme Kinetics Studies
This recombinant QPCT protein could be used to study enzyme kinetics and substrate specificity only if its folding and bioactivity are first experimentally verified. The mammalian expression system may support proper folding, but the N-terminal tag might subtly influence kinetic parameters or substrate access. Without validation (e.g., activity assays using known peptide substrates), kinetic data may be inaccurate. Furthermore, since QPCT has a defined catalytic function in forming pyroglutamate residues, confirmation of its specific activity is essential for meaningful biochemical characterization.
2. Protein-Protein Interaction Studies
The His-tagged protein is technically suitable for pull-down assays to screen for interacting partners. However, the biological relevance of any identified interactions is entirely dependent on the protein's correct folding. If the recombinant QPCT is misfolded, its interaction interfaces could be altered, leading to non-physiological bindings (false positives) or a failure to identify true partners (false negatives). Given that QPCT's interactions, such as with HRAS in renal cell carcinoma, can be functionally significant, ensuring native conformation is critical for valid results. Any interactions discovered require confirmation with native proteins from cellular systems.
3. Antibody Development and Validation
The full-length, high-purity protein is suitable as an immunogen for generating antibodies, particularly those targeting linear epitopes. The mammalian expression system may contribute to the presentation of some conformational epitopes. However, if the protein is misfolded, antibodies generated may not effectively recognize the natively folded, functional QPCT in cells or tissues. The His-tag facilitates purification but could also induce tag-specific antibodies. Validation of any generated antibodies should include testing against the native protein in its physiological context .
4. Structural Biology and Biophysical Analysis
The protein's suitability for high-resolution structural studies (e.g., X-ray crystallography) is strictly dependent on it being properly folded, homogenous, and in the correct oligomeric state. While mammalian expression is beneficial, the >90% purity by SDS-PAGE does not guarantee monodispersity or the absence of aggregates, which are critical for crystallization. The N-terminal tag might potentially influence the N-terminal region or crystal packing. Thorough biophysical characterization (e.g., size-exclusion chromatography, circular dichroism) is a prerequisite to assess folding quality and oligomeric status before embarking on structural studies.
5. In Vitro Assay Development and Screening Applications
This application is fully contingent on confirmed bioactivity. The reliable use of QPCT in assay development or inhibitor screening absolutely requires a functionally active enzyme. If the protein is inactive, screening for inhibitors would be ineffective and lead to misleading results. The tag allows for immobilization in automated platforms, but the functional integrity of the enzyme is the paramount prerequisite. Activity must be verified using established enzymatic assays before the protein is used in any screening endeavor.
Final Recommendation & Action Plan
To ensure reliable and meaningful results, it is strongly recommended to first experimentally validate the folding and bioactivity of this recombinant QPCT protein. The plan should begin with biophysical characterization using size-exclusion chromatography coupled with multi-angle light scattering (SEC-MALS) to assess oligomeric state and monodispersity, and circular dichroism (CD) spectroscopy to analyze secondary structure. This should be followed by functional validation using a standard enzymatic activity assay, for example, by measuring the conversion of a suitable glutaminyl-peptide substrate and determining kinetic parameters, comparing them to literature values if available. If the protein is validated as functional, it can be confidently used for the proposed applications, especially in biochemical and screening contexts relevant to its roles in cancer and neuroscience . If validation fails, its use should be restricted to applications less dependent on native conformation, such as antibody production against linear epitopes, with all limitations clearly disclosed in any subsequent research communications.