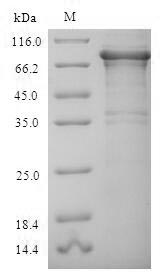
Producing recombinant human replication protein A 70 kDa DNA-binding subunit (RPA1) in E. coli involves co-cloning the target gene (2-616aa of human RPA1) into an expression vector with an N-terminal 6xHis-SUMO-tag gene, which is introduced into E. coli cells. The cells are cultured under conditions that promote protein expression. After sufficient growth, the cells are lysed to release the recombinant RPA1 protein. The collected proteins undergo affinity chromatography purification. The purity of the recombinant RPA1 protein is assessed using SDS-PAGE, exceeding 90%.
Human RPA1 is a crucial component of the Replication Protein A (RPA) complex, which is a heterotrimeric single-stranded DNA-binding protein essential for various DNA processes in eukaryotic cells. RPA1 possesses strong single-stranded DNA binding activity. It plays a critical role in DNA metabolism, including processes such as replication, recombination, and repair [1-3].
RPA1 is crucial for maintaining genomic stability and ensuring accurate DNA replication [5]. Additionally, RPA1 is phosphorylated to facilitate mitotic exit in response to DNA damage during cell division [6]. The complex nature of RPA1, with its multiple functional domains, underscores its importance in DNA replication and repair processes [4] [5].
References:
[1] G. Dodson, Y. Shi, & R. Tibbetts, Dna replication defects, spontaneous dna damage, and atm-dependent checkpoint activation in replication protein a-deficient cells, Journal of Biological Chemistry, vol. 279, no. 32, p. 34010-34014, 2004. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.c400242200
[2] H. He, J. Wang, & T. Liu, Uv-induced rpa1 acetylation promotes nucleotide excision repair, Cell Reports, vol. 20, no. 9, p. 2010-2025, 2017. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2017.08.016
[3] E. Bochkareva, L. Frappier, A. Edwards, & A. Bochkarev, The rpa32 subunit of human replication protein a contains a single-stranded dna-binding domain, Journal of Biological Chemistry, vol. 273, no. 7, p. 3932-3936, 1998. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.273.7.3932
[4] H. Kim and S. Brill, Rfc4 interacts with rpa1 and is required for both dna replication and dna damage checkpoints in saccharomyces cerevisiae, Molecular and Cellular Biology, vol. 21, no. 11, p. 3725-3737, 2001. https://doi.org/10.1128/mcb.21.11.3725-3737.2001
[5] S. Binz and M. Wold, Regulatory functions of the n-terminal domain of the 70-kda subunit of replication protein a (rpa), Journal of Biological Chemistry, vol. 283, no. 31, p. 21559-21570, 2008. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.m802450200
[6] R. Anantha, E. Sokolova, & J. Borowiec, Rpa phosphorylation facilitates mitotic exit in response to mitotic dna damage, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, vol. 105, no. 35, p. 12903-12908, 2008. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0803001105