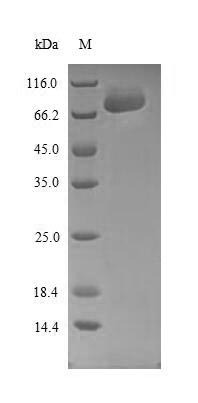
Amino acids 2-444 form the expressed segment for recombinant Human SPRED1. The theoretical molecular weight of the SPRED1 protein is 70.3 kDa. This SPRED1 recombinant protein is manufactured in e.coli. Fusion of the N-terminal 10xHis-SUMO tag and C-terminal Myc tag into the SPRED1 encoding gene fragment was conducted, allowing for easier detection and purification of the SPRED1 protein in subsequent stages.
Human sprouty-related, EVH1 domain-containing protein 1 (SPRED1) primarily functions as a negative regulator of the RAS-MAPK signaling pathway, crucial for cellular proliferation and differentiation. SPRED1 inhibits the activation of RAF kinases, attenuating downstream signaling. In medical research, SPRED1 is associated with Neurofibromatosis Type 1 (NF1) and Legius syndrome, providing insights into these genetic disorders. In cancer biology, SPRED1's role in suppressing MAPK signaling may have implications for tumor development and progression. Investigating SPRED1 contributes to understanding its regulatory functions, offering potential applications in cancer research, and developmental biology, and providing a molecular basis for therapeutic interventions targeting aberrant RAS-MAPK signaling pathways.