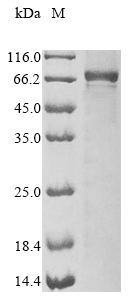
The gene responsible for the mouse interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 3 (Irak3) protein (1-609aa) is co-incorporated into a plasmid vector with the N-terminal 10xHis-tag gene and the C-terminal Myc-tag gene, forming a recombinant plasmid. The resulting recombinant plasmid is introduced into baculovirus cells, from which cells survive in the presence of a specific antibiotic are selected. The selected baculovirus cells containing the recombinant plasmid are cultured under conditions that facilitate the expression of the target gene. After expression, affinity purification is used to isolate and purify the recombinant mouse Irak3 protein from the cell lysate. Denaturing SDS-PAGE is employed to resolve the resulting recombinant mouse Irak3 protein, revealing a purity greater than 85%.
IRAK3, also called interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 3, is a protein that helps steer the body's initial immune response and tackle inflammation. It's like a traffic cop for inflammatory signals and is linked to conditions like sepsis [1]. IRAK3 acts as a brake on certain immune pathways, keeping the production of inflammatory substances in check and helping maintain a balance in the body's response to inflammation [2]. In some cancers, it puts the brakes on the immune system, allowing cancer cells to evade destruction [3]. Plus, it's a key player in regulating the body's initial immune response, especially in conditions like obesity and metabolic syndrome [4]. By tweaking certain immune signals, it could give clues about how inflammation might progress [5]. In the world of cancer, it helps control how signals move around and how the immune system responds within tumors, which could affect cancer treatments [6].
References:
[1] T. Nguyen, I. Turek, T. Meehan-Andrews, A. Zacharias, & H. Irving, Analysis of interleukin-1 receptor associated kinase-3 (irak3) function in modulating expression of inflammatory markers in cell culture models: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Plos One, vol. 15, no. 12, p. e0244570, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0244570
[2] P. Cohen, The tlr and il-1 signalling network at a glance, Journal of Cell Science, 2014. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.149831
[3] L. Freihat, V. Muleya, D. Manallack, J. Wheeler, & H. Irving, Comparison of moonlighting guanylate cyclases: roles in signal direction?, Biochemical Society Transactions, vol. 42, no. 6, p. 1773-1779, 2014. https://doi.org/10.1042/bst20140223
[4] M. Hulsmans, B. Geeraert, D. Keyzer, A. Mertens, M. Lannoo, B. Vanaudenaerdeet al., Interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase-3 is a key inhibitor of inflammation in obesity and metabolic syndrome, Plos One, vol. 7, no. 1, p. e30414, 2012. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0030414
[5] L. Freihat, J. Wheeler, A. Wong, I. Turek, D. Manallack, & H. Irving, Irak3 modulates downstream innate immune signalling through its guanylate cyclase activity, Scientific Reports, vol. 9, no. 1, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-51913-3
[6] G. Tunali, M. Bedós, D. Nagarajan, P. Fridh, I. Papakyriacou, & Y. Mao, Il-1 receptor–associated kinase-3 acts as an immune checkpoint in myeloid cells to limit cancer immunotherapy, Journal of Clinical Investigation, vol. 133, no. 7, 2023. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci161084"