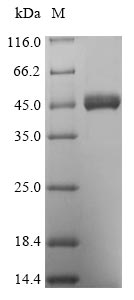
The production of this Recombinant Mouse Txnip protein required the insertion of a DNA fragment (Txnip, 1-397aa) into the plasmid vector and the transferral of this vector into Yeast cells (the step of transformation). The cells were then cultured and induced to express the Txnip protein. This recombinant protein was fused with N-terminal 6xHis tag. Its purity is 90%+ determined by SDS-PAGE.
Txnip (Txnip or Vdup1) is a gene providing an instruction of making a protein named thioredoxin-interacting protein (Txnip) in mus musculus (mouse). This gene has many orthologs in multiple mammals, such as human, norway rat, pig, cattle, etc. The protein encoded by this gene is also known as vitamin D3 up-regulated protein 1 and belongs to arrestin family.Txnip protein inhibits the antioxidative function of thioredoxin by its enzyme inhibitor activity and leads to the accumulation of reactive oxygen species and cellular stress. This protein is involved multiple biological processes, including cell cycle, cellular response to tumor cell, response to oxidative stress, etc.