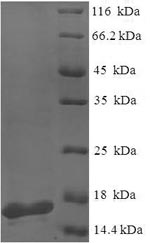
The recombinant Pseudomonas aeruginosa lecA protein is a fusion protein consists of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa lecA protein (2-122aa) partnered with the N-terminal 6xHis tag. It was produced in the E.coli. This recombinant lecA protein's purity is greater than 90% determined by SDS-PAGE. After electrophoresis, there is a 16 kDa protein band presented on the gel.
LecA is a cytotoxic lectin and adhesin produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa which binds hydrophobic galactosides with high specificity and affinity. Certain research showed that lecA is expressed in biofilm-grown cells. The carbohydrate-binding protein LecA from Pseudomonas aeruginosa plays an important role in the formation of biofilms in chronic infections. Development of inhibitors to disrupt LecA-mediated biofilms is desired but it is limited to carbohydrate-based ligands. Moreover, discovery of drug-like ligands for LecA is challenging because of its weak affinities. Lectins are carbohydrate-binding proteins with diverse functions that are found in all domains of life. Lectins are involved in the infection process of the Gram-negative bacterium Pseudomonas aeruginosa, an important member of the often highly drug-resistant ESKAPE pathogens. The two bacterial lectins LecA and LecB, are virulence factors that are important for bacterial adhesion. LecA and LecB, which can be specific for galactose and fucose (Fuc), respectively. The affinity of Fuc and LecB was much higher than that of galactose and LecA. Multiple saccharin and saccharide inhibitors targeting LecB have successfully applied to treat P. aeruginosa infection.