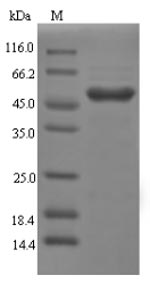
Recombinant Rat Galectin-4 (Lgals4) is produced using an E.coli expression system and contains the complete sequence spanning amino acids 1-324. The protein comes with an N-terminal 6xHis-SUMO tag, which appears to improve both solubility and purification efficiency. SDS-PAGE analysis shows purity levels above 90%, which should provide reliable results for most research applications. This product is intended for research use only.
Galectin-4 belongs to the galectin family and is known for its ability to bind β-galactoside sugars. The protein seems to play important roles in several cellular processes, including cell adhesion and immune response regulation. Studies suggest that Galectin-4 may influence signaling pathways and cellular communication, making it a useful research tool for those working in cellular biology and immunology.
Potential Applications
Note: The applications listed below are based on what we know about this protein's biological functions, published research, and experience from experts in the field. However, we haven't fully tested all of these applications ourselves yet. We'd recommend running some preliminary tests first to make sure they work for your specific research goals.
Based on the provided information, the recombinant Rat Galectin-4 (Lgals4) is expressed in E. coli without any tags. While the tag-free nature is advantageous for maintaining native protein structure, E. coli remains a prokaryotic system generally unsuitable for producing properly folded eukaryotic carbohydrate-binding proteins like galectin-4. This protein requires precise folding with two carbohydrate recognition domains (CRDs) and proper disulfide bond formation for its lectin activity. The protein is full-length (1-324aa) with >85% purity, but E. coli lacks eukaryotic chaperones and quality control machinery. Since activity is unverified, the protein cannot be assumed to be correctly folded or bioactive without experimental validation.
1. Protein-Protein Interaction Studies
This tag-free recombinant rat galectin-4 can be utilized in protein-protein interaction studies through methods such as co-immunoprecipitation or label-free binding assays. The absence of tags avoids potential steric hindrance or artificial interactions that tagged proteins might introduce, better preserving native binding interfaces. Researchers can incubate the recombinant protein with cell lysates or purified candidate binding partners to identify interaction networks involving galectin-4 in carbohydrate recognition and signaling pathways. However, if the protein is misfolded (as is possible with E. coli expression), interactions may not reflect physiological binding relationships. Such studies should therefore include proper controls and validation with native galectin-4 when possible. The >85% purity helps minimize non-specific background binding during interaction experiments.
2. Antibody Development and Validation
This tag-free recombinant rat galectin-4 represents an excellent immunogen for generating antibodies specific to the native protein. The absence of tags ensures antibodies will target authentic galectin-4 epitopes without tag interference. The high purity (>85%) and full-length structure support effective immunization protocols. However, if the protein is misfolded in E. coli (a significant risk), the resulting antibodies may not recognize conformational epitopes of properly folded galectin-4 in rat tissues. Validation against native protein remains essential.
3. Biochemical Characterization and Functional Assays
The tag-free nature makes this galectin-4 highly suitable for biochemical studies, including thermal stability, pH sensitivity, and structural analyses. However, carbohydrate-binding experiments require proper folding to be physiologically relevant. If galectin-4 is misfolded, binding preferences will not reflect native specificity. Functional assays should only be conducted after validating proper folding through biophysical methods and positive controls with known galectin ligands.
4. Comparative Species Studies
This application is highly problematic without folding validation. While the tag-free protein is ideal for evolutionary comparisons in principle, if the rat galectin-4 is misfolded, comparisons with properly folded proteins from other species will yield invalid evolutionary insights. Structural and functional comparisons require all proteins in the comparison to be natively folded. This application should be deferred until proper folding is confirmed.
Final Recommendation & Action Plan
Given the confirmation that this is a tag-free protein, first perform comprehensive biophysical characterization (circular dichroism for secondary structure, analytical ultracentrifugation for oligomeric state) to assess folding quality. Validate carbohydrate-binding activity using known galectin ligands (e.g., lactose, specific glycans) before functional studies. Antibody development can proceed immediately as the highest-priority application. Avoid comparative and interaction studies until proper folding is confirmed. For reliable structural and functional studies, consider validating with galectin-4 from eukaryotic expression systems. The tag-free nature is advantageous but doesn't guarantee proper folding in E. coli.